Invoice Ninja Deserialization Flaw (CVE-2024-55555)

Overview
The SonicWall Capture Labs threat research team became aware of the threat CVE-2024-55555, assessed its impact, and developed mitigation measures for this vulnerability.
CVE-2024-55555 is a critical insecure deserialization vulnerability in Invoice Ninja affecting version 5.10.42, allowing authenticated attackers with knowledge of the application’s APP_KEY to inject malicious PHP objects through the /route/{hash} endpoint and achieve remote code execution via gadget-chain exploitation. Classified under CWE-502 (Deserialization of Untrusted Data) and rated High on the CVSS 3.1 scale, the vulnerability arises from Laravel’s decrypt() function automatically invoking unserialize() on user-supplied encrypted data without validation. This enables PHP Object Injection (POI) attacks that can trigger arbitrary code execution through magic methods such as __destruct() and __wakeup() in loaded dependencies, including Laravel Framework v11, Symfony components, Guzzle, and Monolog. The vulnerable /route/{hash} endpoint decrypts the hash parameter using AES-256-CBC encryption, deserializes the plaintext, and uses it as a redirect target, creating an attack surface where crafted gadget chains from phpggc or custom exploit chains can bypass application security controls, access internal resources, or execute arbitrary system commands. Disclosed in October 2024, the issue is mitigated in version 5.10.43 by completely removing the vulnerable endpoint from routes/client.php. Users running v5.10.42 should upgrade immediately, as no effective workarounds exist. The presence of the APP_KEY in configuration files or environment variables represents a critical attack prerequisite that must be protected.
Technical Overview
The vulnerability in Invoice Ninja v5.10.42 exists in the `/route/{hash}` endpoint located in `routes/client.php` at lines 147-160. This endpoint accepts a user-supplied encrypted hash parameter, decrypts it using Laravel's `decrypt()` function, and uses the resulting value as a redirect target without any validation or sanitization. The critical security flaw lies in Laravel's `decrypt()` implementation, which automatically calls PHP's `unserialize()` function on the decrypted data. This creates an insecure deserialization vulnerability where an attacker who possesses the application's `APP_KEY` can craft malicious encrypted payloads containing serialized PHP objects that, when deserialized, can execute arbitrary code through gadget chain exploitation.
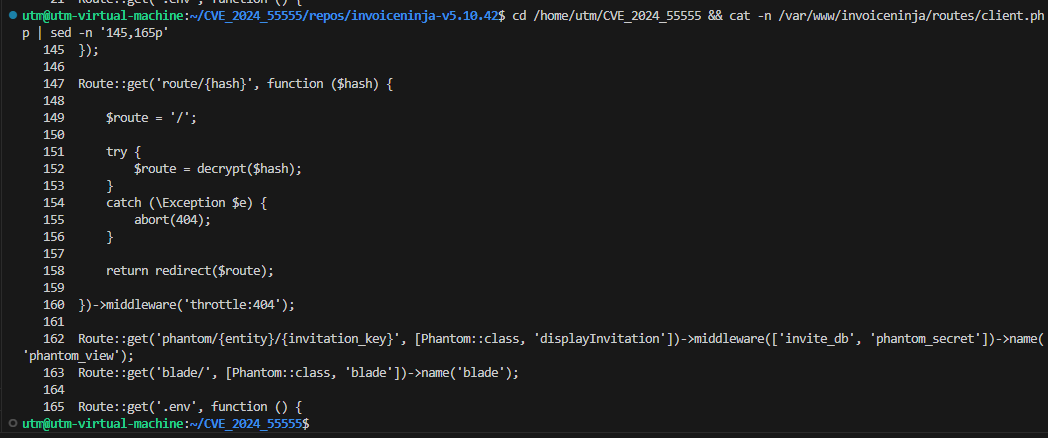
The vulnerability manifests through a multi-step attack chain: First, Laravel's `decrypt()` function (line 152) receives the encrypted `$hash` parameter and performs AES-256-CBC decryption using the application's `APP_KEY`. Second, after successful decryption and HMAC verification, Laravel automatically invokes `unserialize()` on the decrypted plaintext, a behavior inherited from Laravel's encryption implementation. Third, when PHP deserializes the data, any objects in the serialized payload are instantiated, and their magic methods (`__wakeup()`, `__destruct()`, `__toString()`, etc.) are automatically triggered. Finally, if the attacker crafts a gadget chain using existing classes in Invoice Ninja's dependencies (such as Laravel Framework v11, Symfony components, Guzzle HTTP client, or Monolog logger), these magic methods can be chained together to achieve arbitrary code execution. The `redirect($route)` call on line 158 becomes irrelevant in this attack scenario because the malicious code executes during the deserialization phase, before the redirect occurs. The throttle middleware on line 160 provides limited protection since an attacker only needs a single successful exploitation attempt to compromise the system.
The patch implemented in Invoice Ninja v5.10.43 takes a definitive approach to remediation by completely removing the vulnerable endpoint rather than attempting to sanitize or validate its input. This design decision reflects the principle that the most secure code is code that does not exist, eliminating the attack surface entirely rather than trying to defend it. The vulnerable route is commented out in the patched version, effectively preventing any incoming HTTP requests from reaching the insecure deserialization code path. This approach ensures that even if an attacker possesses the application's `APP_KEY` and has the technical capability to generate valid encrypted payloads, there is no longer an accessible endpoint to receive and process these malicious requests.
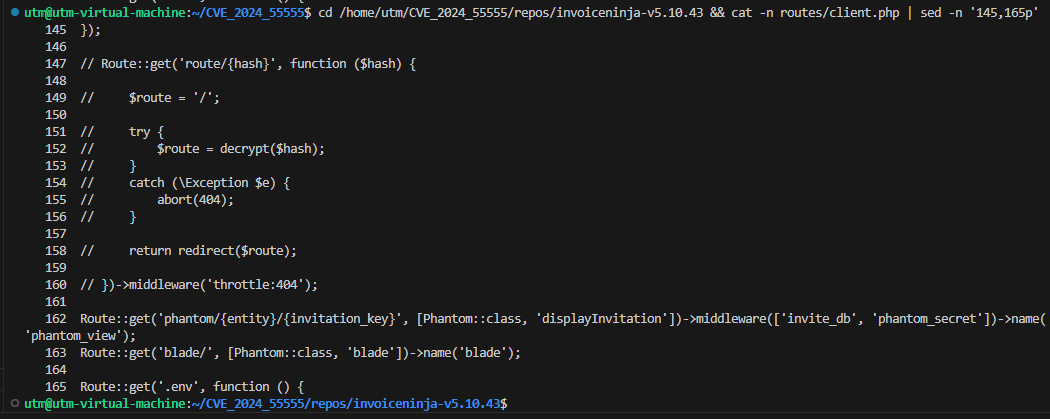
The remediation strategy demonstrates several security best practices and architectural decisions. By commenting out rather than deleting the vulnerable code, the development team preserves institutional knowledge about the vulnerability while preventing its exploitation, which aids in security audits and future code reviews. The patch avoids introducing complexity through input validation, whitelisting, or additional middleware that could themselves contain vulnerabilities or bypassable logic. From a defense-in-depth perspective, this elimination approach is superior to partial mitigations such as route validation or redirect target whitelisting, as those would still maintain the dangerous deserialization code path in an active state. The fix also implicitly addresses the secondary vulnerability of open redirect since the entire endpoint responsible for redirection is removed. Organizations deploying this patch can clear their Laravel route cache using `php artisan route:clear` to ensure the commented route is not cached in the application's routing table, and should verify that HTTP requests to `/route/*` patterns return 404 Not Found responses, confirming that the attack vector is no longer accessible from the network perimeter.
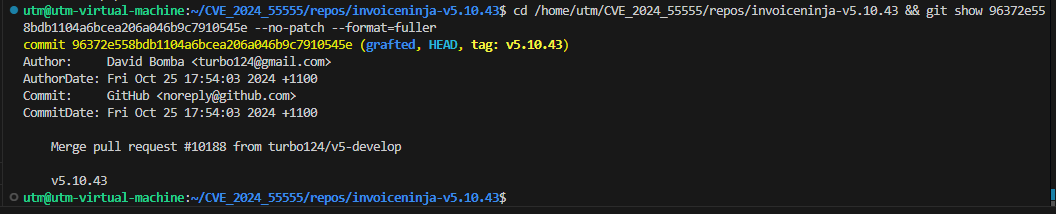
The security patch was committed by David Bomba (turbo124@gmail.com) on October 25, 2024, at 17:54:03 UTC+11 (Australian Eastern Daylight Time). The commit is tagged as `v5.10.43` and represents a merge from the development branch (`v5-develop`) into the production release, as indicated by the merge pull request reference #10188. The commit was authored by David Bomba but committed via GitHub's noreply service account, suggesting it was merged through GitHub's web interface or automated merge system. The brief time span between the vulnerable version (v5.10.42) and the patched version (v5.10.43) suggests this was treated as a high-priority security fix requiring rapid deployment. Organizations can verify they have received this security update by checking their local Invoice Ninja installation's VERSION.txt file or by running `git log` to confirm this commit hash is present in their deployment history.
Triggering the Vulnerability
The following conditions must be met for successful exploitation of CVE-2024-55555:
• Invoice Ninja version is v5.10.42: The vulnerable version with the insecure `/route/{hash}` endpoint enabled and uncommented in `routes/client.php`.
• Knowledge of APP_KEY: The attacker must possess the application's encryption key stored in the `.env` file, typically a 32-byte base64-encoded secret. This key can be obtained through configuration file disclosure vulnerabilities, leaked backups, exposed version control repositories, insider access, or server compromise.
• Exploitable gadget chains present: Invoice Ninja must have dependencies containing classes with exploitable magic methods that can be chained together for code execution. The application includes Laravel Framework v11, Symfony components (HTTP client, mailers), Guzzle HTTP v7.2, and potentially Monolog, all of which have known gadget chains documented in tools like phpggc.
• Network access to the vulnerable endpoint: The attacker must be able to send HTTP GET requests to `http://[target]/route/{encrypted_payload}`. This requires network connectivity to the Invoice Ninja instance, which could be over the internet, a VPN, or an internal network, depending on deployment.
• PHP deserialization capabilities: The target server must be running PHP (version 8.2+ as required by Invoice Ninja v5.10.42) with standard deserialization functions enabled. The `unserialize()` function must not be disabled via `disable_functions` in `php.ini` (though this is rarely disabled as it would break legitimate application functionality).
Exploitation
The vulnerability can be exploited through multiple attack vectors depending on the attacker's capabilities and objectives. The primary attack vector involves crafting a malicious PHP object serialization payload using gadget chains from Invoice Ninja's dependencies (Laravel Framework v11, Symfony components, Guzzle HTTP, Monolog), encrypting this payload using the known `APP_KEY` with Laravel's AES-256-CBC encryption scheme, and sending it to the vulnerable `/route/{hash}` endpoint. Tools such as phpggc provide pre-built gadget chains for common PHP frameworks, making exploitation accessible even to attackers without deep PHP internal knowledge. Secondary exploitation vectors include leveraging the open redirect aspect of the vulnerability for phishing campaigns, session token theft, or CSRF attacks that trick authenticated users into visiting malicious URLs. The vulnerability is particularly dangerous in hosted or multi-tenant environments where a single compromised instance could be used to pivot to other tenants or infrastructure components.
SonicWall Protections
To ensure SonicWall customers are prepared for any exploitation that may occur due to this vulnerability, the following signatures have been released:
- IPS: 21542 Invoice Ninja Insecure Deserialization
Remediation Recommendations
The risks posed by CVE-2024-55555 can be mitigated or eliminated by:
• Upgrade Invoice Ninja: Promptly move to version 5.10.43 or later, which completely removes the vulnerable `/route/{hash}` endpoint from the application codebase.
• Rotate APP_KEY: Immediately regenerate the Laravel `APP_KEY` in the `.env` file using `php artisan key:generate` to invalidate any previously crafted malicious payloads, as exploitation requires knowledge of this secret key.
• Restrict network access: Bind Invoice Ninja to trusted network segments only, implement IP allowlisting at the firewall or web server level, and require VPN access for remote administration to limit attack surface.
• Utilizing IPS signatures: to detect and block malicious payloads targeting this vulnerability.
• Principle of least privilege: Run the web server and PHP-FPM processes with minimal filesystem permissions, ensuring the `www-data` user cannot write to sensitive directories outside `storage/` and `bootstrap/cache/`.
Relevant Links
CVE Overview
Github Commit d930202
CWE-502 Deserialization of Untrusted Data
National Vulnerability Database (NVD) Entry
CVSS v3.1 Calculator
EPSS Score History
Share This Article

An Article By
An Article By
Security News
Security News
