Exploited in the Wild: DELMIA Apriso Insecure Deserialization (CVE-2025-5086)

Overview
The SonicWall Capture Labs threat research team became aware of a deserialization of untrusted data vulnerability in DELMIA Apriso, assessed its impact and developed mitigation measures. DELMIA Apriso, developed by Dassault Systèmes, is a Manufacturing Operations Management (MOM) software that helps manufacturers digitize and manage global production. A critical vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2025-5086, has been discovered in DELMIA Apriso, affecting software versions from Release 2020 through Release 2025. This vulnerability allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code by injecting a malformed serialized payload, posing a severe threat to system integrity.
SonicWall sensors have detected a significant volume of active exploitation attempts targeting this flaw and it has been added to CISA’s Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog. Users are strongly advised to update their DELMIA Apriso instances to the latest patched version immediately, as outlined in the vendor’s official advisory.
Technical Overview
DELMIA Apriso is built on Microsoft's .NET Framework and uses various web services to provide manufacturing operations management capabilities. It's designed to manage and optimize manufacturing processes in real-time, making it a critical component in modern industrial environments. This integration with enterprise systems and its widespread deployment in critical industries makes it an attractive target for attackers.
This vulnerability arises from unsafe deserialization of untrusted data which is a well-known class of security flaws. In .NET environments, several serializers can introduce significant risk if used without proper validation. For instance,
- BinaryFormatter - Known to be unsafe and officially deprecated in modern .NET
- NetDataContractSerializer - Serializes type metadata along with the data, which attackers can abuse for type confusion and arbitrary code execution.
- JsonConvert with TypeNameHandling - Can be exploited to load attacker-specified types if improperly configured.
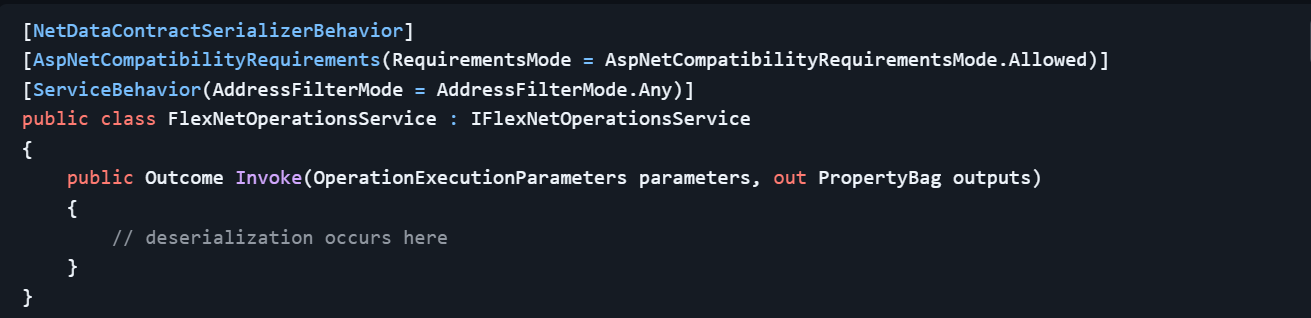
The specific vulnerability lies within the FlexNetOperationsService.svc Windows Communication Foundation (WCF) service, implemented in the following file path:
FlexNet.WebUI.WebServicecs/FlexNetOperationsService.cs
This WCF service uses the NetDataContractSerializer, which includes .NET type metadata in the serialized XML data, allowing attackers to control the types being deserialized. The vulnerable service configuration structure is shown below in Figure 1. Notably, the vulnerable endpoint is accessible publicly as well as do not require authentication.
Triggering the Vulnerability
An attacker can exploit this vulnerability by following the steps below:
- The vulnerable installation needs to be accessible remotely.
- Create a malicious SOAP request and submit it to the vulnerable HTTP(S) endpoint: /apriso/WebServices/FlexNetOperationsService.svc/Invoke
- The service deserializes malicious data using NetDataContractSerializer
- The embedded arbitrary code would be executed.
Exploitation
Successful exploitation of this vulnerability allows a remote attacker to achieve Remote Code Execution by exploiting the underlying .NET deserialization flaw within DELMIA Apriso. The attack leverages a carefully crafted serialized payload that, when processed by the vulnerable service, results in arbitrary code execution on the target system. The structure of the exploitation payload request is quite sophisticated as seen in Figure 2. A full example of the exploit request is available on the hacktron blog.
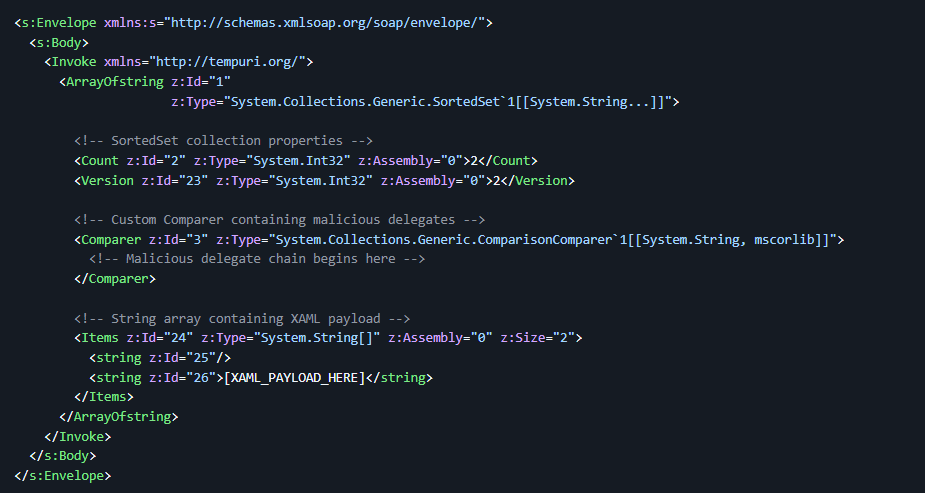
The major components of the payload are:
- SortedSet Gadget: Uses System.Collections.Generic.SortedSet as entry point
- Delegate Chaining: Chains delegates to control execution flow
- XAML Parser: Leverages System.Windows.Markup.XamlReader.Parse for code execution
- Assembly Loading: Uses compressed payload to load and execute arbitrary assemblies
According to SonicWall sensors data, SANS Internet Storm Center, and the CISA Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog, this vulnerability is currently under active exploitation by threat actors. The combination of public exposure, lack of authentication, and RCE capabilities makes this flaw particularly dangerous for unpatched instances.
SonicWall Protections
To ensure SonicWall customers are prepared for any exploitation that may occur due to this vulnerability, the following signatures have been released:
- IPS: 21462 Dassault Systems DELMIA Apriso Insecure Deserialization
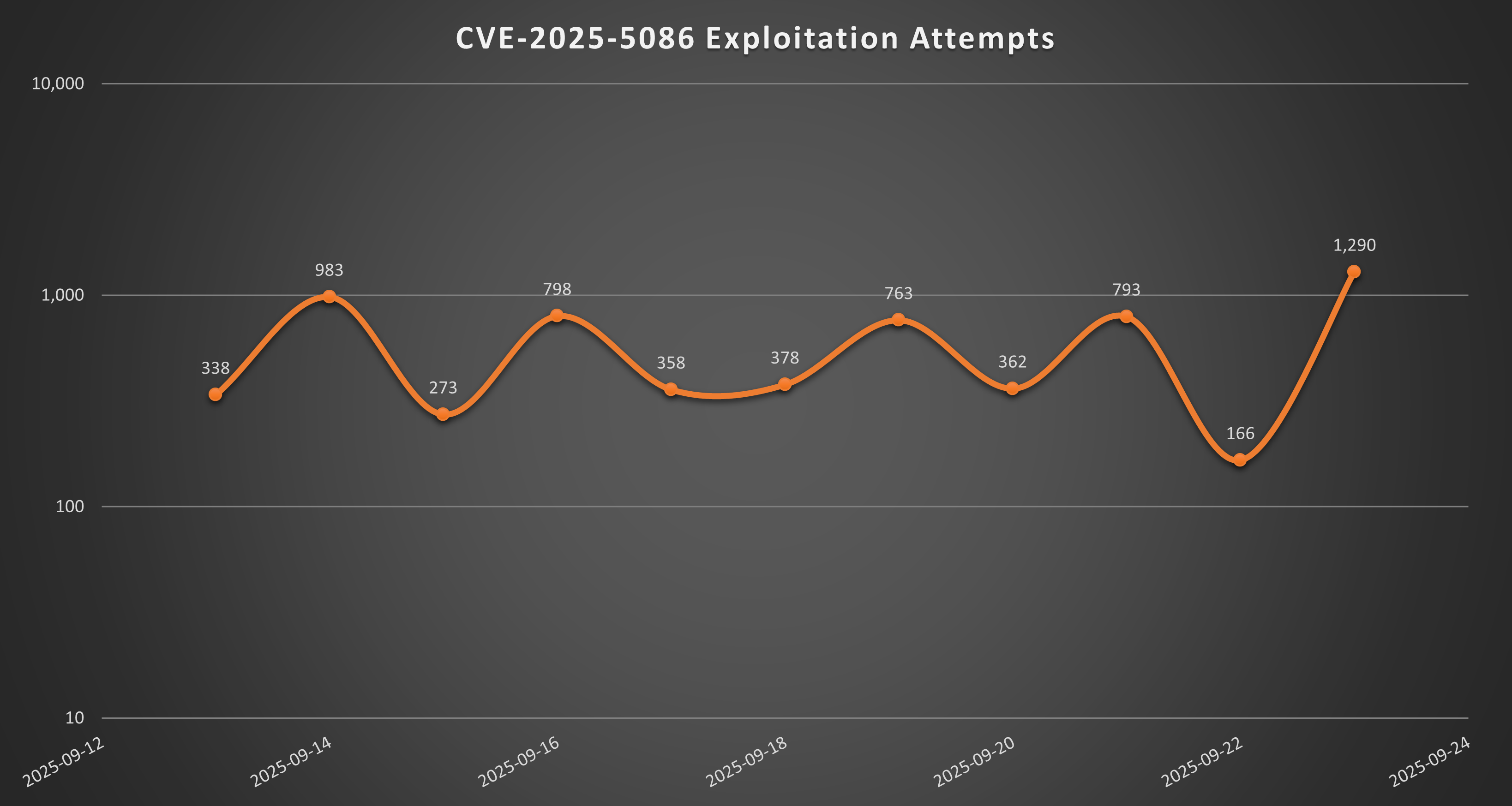
Threat Graph
The SonicWall sensor data shows a considerable number of exploit attempts, indicating the popularity of the affected software among the threat actors.
Remediation Recommendations
DELMIA Apriso users are strongly advised to upgrade their instances to the latest patched version as outlined in the official vendor advisory.
Relevant Links
Share This Article

An Article By
An Article By
Security News
Security News
