"Ni8mare" - RCE Vulnerability in N8n AI Workflow Automation (CVE-2026-21858)

Overview
The SonicWall Capture Labs threat research team became aware of a Critical unauthenticated file read vulnerability in n8n – a flexible AI workflow automation platform, assessed their impact, and developed mitigation measures. n8n is frequently used to automate repetitive operational tasks and to integrate security tools and SaaS platforms. In simple words, using n8n users build workflows composed of nodes, with each node representing an action such as making an API request, processing data, or sending an email.
The unauthenticated file read vulnerability, identified as CVE-2026-21858, has been discovered in n8n AI workflow automation, affecting versions starting with 1.65.0 and below 1.121.0. These flaws enable remote attackers to access files on the underlying server through unauthenticated file access via improper webhook request handling. Dubbed as “Ni8mare”, this unauthenticated vulnerability has received a CVSS score of 10 (Critical) due to its low attack complexity, high impact, and the fact that it affects core application functionality. As described in PoC, the impact of unauthenticated file access can result into arbitrary file read, forge admin JWT, Sandbox bypass or even Remote Code Execution. Targeting AI-powered workflow automation platforms introduces a new attack vector, which may create additional opportunities for threat actors leading to data breaches and malicious code distribution. Hence, all organizations that use n8n AI workflow instances are strongly encouraged to update their instances to the latest patched version as a matter of urgency.
Technical Overview
At the heart of vulnerability lies the core issue: n8n webhook handlers and file upload parsers. The custom web forms implement file uploads without validating the content type also termed as Content-Type confusion flaw. In N8n instance, a webhook gathers incoming data for any workflow defined by nodes. A webhook is a component that enables interaction between web applications and services via custom call backs. This suggests that an application does not have to wait unnecessarily for any event such as a patch update, data shall be pushed automatically over HTTP messages whenever such event occurs. These webhooks can optionally support file uploads, typically parsed when requests are sent.
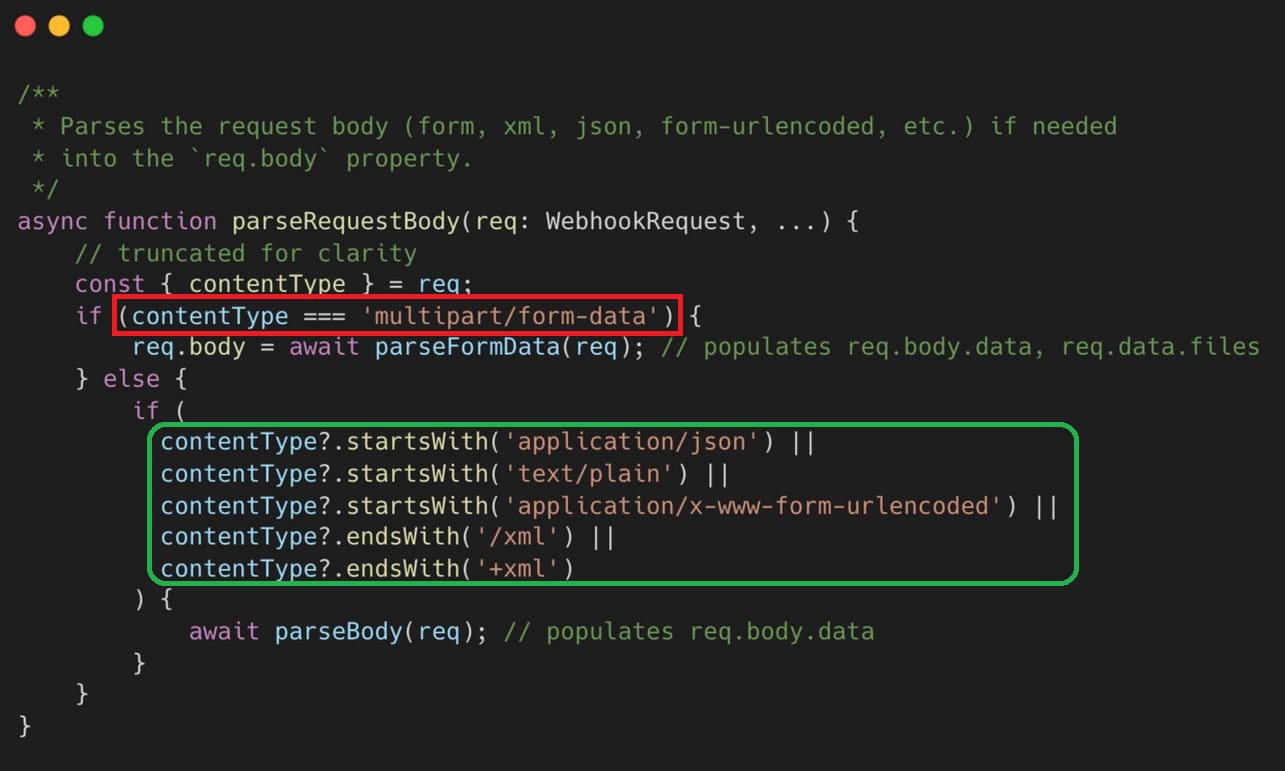
As shown in Figure 1 for multipart/form-data requests, the application relies on the parseFormData() function, while all other content types are handled by parseBody (). The former one acting as file upload parser and starting point of this critical vulnerability.
As coined earlier, improper validation of the Content-Type header allows attackers to corrupt the internal request-parsing state, opening unintended file access and execution paths. By crafting malicious HTTP requests with manipulated content types and payload structures, an attacker can bypass internal safeguards, read sensitive files such as authentication secrets, forge administrator sessions, and ultimately execute arbitrary code on the host system. The consequences are severe, ranging from full server compromise and credential theft to lateral movement across connected services—all without requiring any authentication.
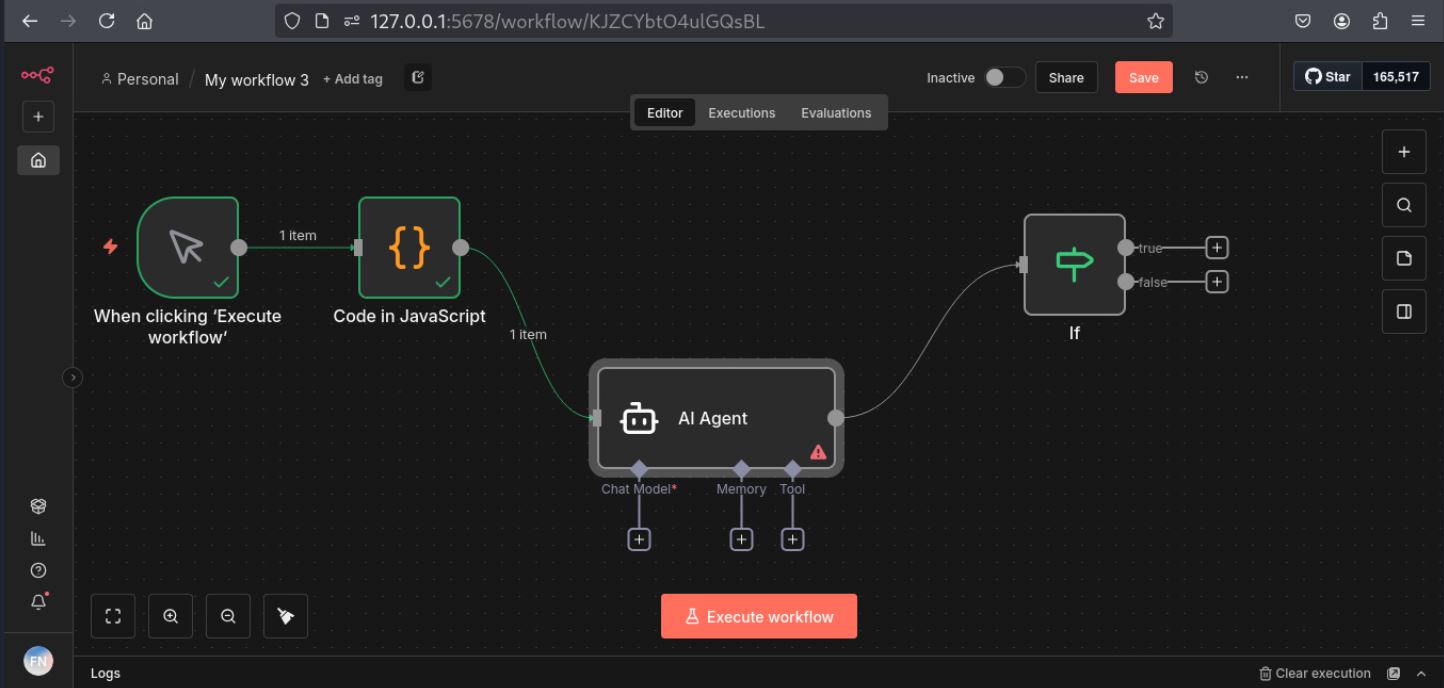
Technically, an n8n workflow is a directed graph of nodes as shown in Figure 2. According to needs of a user, it can select node and formulate a workflow. A simple workflow could be a scheduled trigger event, an HTTP request, a Slack node or a simple Function node.
In ideal conditions n8n webhooks processes data as below:
- Uploaded files are parsed by a multipart parser
- File data is populated in req.body.files
- Downstream nodes rely on this structure to safely access uploads
But certain webhook handlers access req.body.files without validating the request’s content type. Due to Content-Type Confusion flaw, HTTP requests sent as application/json or xml can still supply a crafted files object. Once attackers gain full control over the req.body.files structure, n8n loses the ability to differentiate legitimate file uploads from attacker-supplied file references. By redirecting file paths to arbitrary locations on the local filesystem, an attacker can force the application to read sensitive data directly from disk. This enables access to internal configuration files and embedded databases that are not intended to be reachable via webhook-driven workflows.
This stage is pivotal, as it exposes the secrets and state required to escalate privileges and progress toward full system compromise.
Exploitation
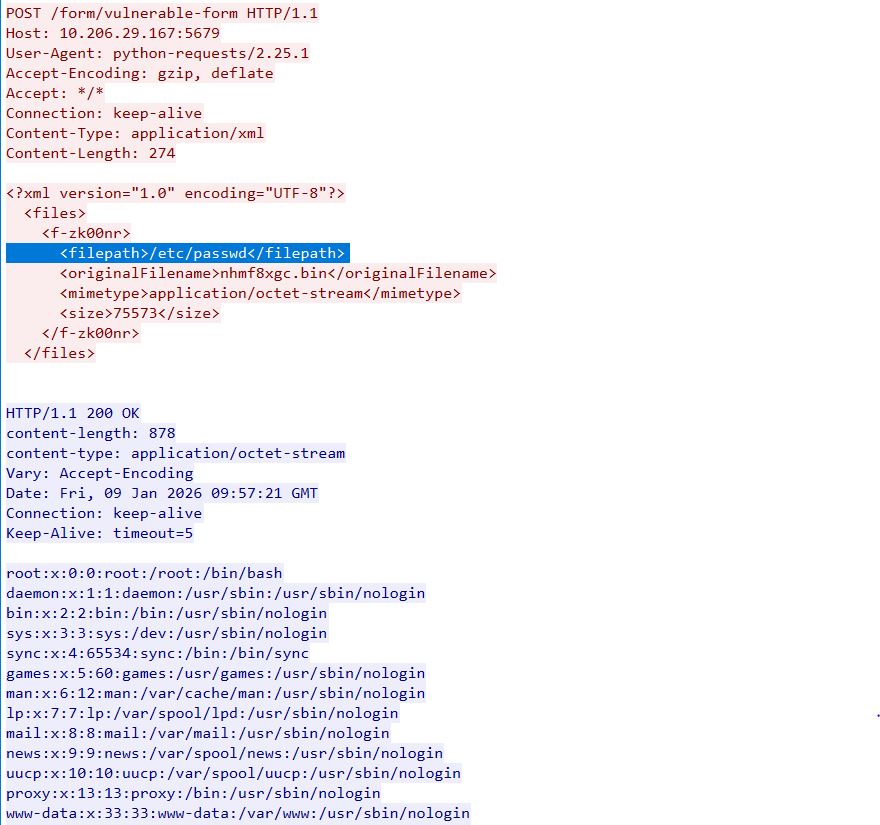
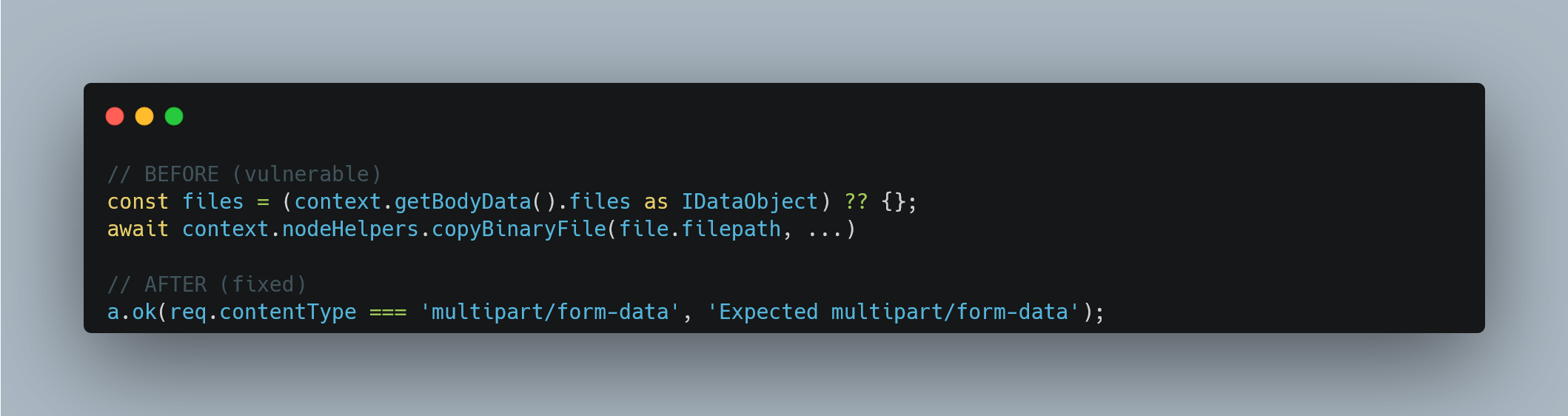
Successful exploitation of CVE-2026-21858 allows remote, unauthenticated attackers to achieve Remote Code Execution (RCE) in vulnerable N8n AI workflow instances. As demonstrated in Figure 3, an attacker having access to a vulnerable N8n platform, starts the exploit chain by intercepting the HTTP request sent when uploading a file through the Form and change the content-type from multipart/form-data to something else (like application/xml). The attacker can craft request body to control the req.body.files object. The patched system will reject such requests, which introduces additional safeguards to restrict expression evaluation.
SonicWall Protections
To ensure SonicWall customers are prepared for any exploitation that may occur due to this vulnerability, the following signatures have been released:- IPS:21846 - n8n Webhook Request Unauthenticated File Access
- IPS:21847 - n8n Webhook Request Unauthenticated File Access 2
- IPS:21849 - n8n Webhook Request Unauthenticated File Access 3
- IPS:21799 - n8n Remote Code Execution
Remediation Recommendations
Given that adversary can circumvent access controls allowing them to access sensitive files with ease, users are strongly advised to upgrade their instances to the latest patched version as outlined in the official vendor advisory.
Relevant Links
Share This Article

An Article By
An Article By
Dhiren Vaghela
Dhiren Vaghela
Dhiren Vaghela has over a decade of experience in the IPS domain, with a strong focus on defensive security. His expertise lies in identifying, analyzing and mitigating vulnerabilities. Dhiren is well-versed in content-based signature writing, scanner-based alert generation and technical blog writing. By leveraging emerging technologies, he has developed numerous IPS signatures across various protocols. Known for his exceptional signature writing skills and collaborative team spirit, Dhiren is a valuable asset in the field of cybersecurity.
