N8N AI Workflow Automation Remote Code Execution Vulnerability (CVE-2025-68613)

Overview
The SonicWall Capture Labs threat research team became aware of a Critical Remote Code Execution (RCE) Vulnerability in n8n, a flexible AI workflow automation platform, assessed its impact, and developed mitigation measures. N8N is frequently used to automate repetitive operational tasks and to integrate security tools and SaaS platforms. In simple words, using n8n users build workflows composed of nodes, with each node representing an action such as making an API request, processing data, or sending an email.
The authenticated RCE vulnerability, identified as CVE-2025-68613, has been discovered in n8n AI workflow automation, affecting versions starting with 0.211.0 and prior to 1.120.4, 1.121.1, and 1.122.0 in its server-side expression evaluation engine. These flaws enable remote attackers to exploit the built-in node(s) feature to achieve code execution on the local host. With ease and a high exploitability rate, authenticated threat actors can exploit the vulnerability to achieve code execution via node abuse on the host. Though being an authenticated vulnerability, CVE-2025-68613 received a CVSS score of 9.9 (Critical) due to its low attack complexity, high impact, and the fact that it affects core application functionality. Exploitation requires authentication, but no elevated privileges beyond those required for workflow creation or editing. Targeting AI-powered workflow automation platforms introduces a new attack vector, which may create additional opportunities for threat actors, leading to data breaches and the distribution of malicious code. Hence, all organizations that use n8n AI workflow instances are strongly encouraged to update their instances to the latest patched version as a matter of urgency.
Technical Overview
At the heart of vulnerability lies the core issue: the expression evaluation engine. n8n is frequently used to automate repetitive operational tasks and to integrate security tools and SaaS platforms. The n8n AI workflow platforms can be deployed in a variety of configurations, such as:
- Self-hosted instances
- n8n.cloud, i.e. Cloud-hosted
- Internal automation tools
While understanding the architecture of n8n, it is built on Node.js, using JavaScript for platform internals and user workflow logic. The primary architecture is built on,
- Workflow Execution Engine
- Expression Evaluation System: Processes dynamic expressions wrapped in double curly braces {{}} that are evaluated as JavaScript code during workflow execution.
- Code Nodes: Allow users to write custom JavaScript or Python code as workflow steps, extending platform capabilities.
- 400+ Native Integrations: Pre-built connectors to various APIs and services that form the nodes in workflows.
Technically, an n8n workflow is a directed graph of nodes as shown in Figure 1. According to the user's needs, they can select a node and formulate a workflow. A simple workflow can be triggered by a scheduled event, an HTTP request, a slack node, or a basic function node. As mentioned earlier, the Expression Evaluation System accepts function expressions that execute in a context that is not properly sandboxed, breaking the boundary between “server-code” and an “expression”.
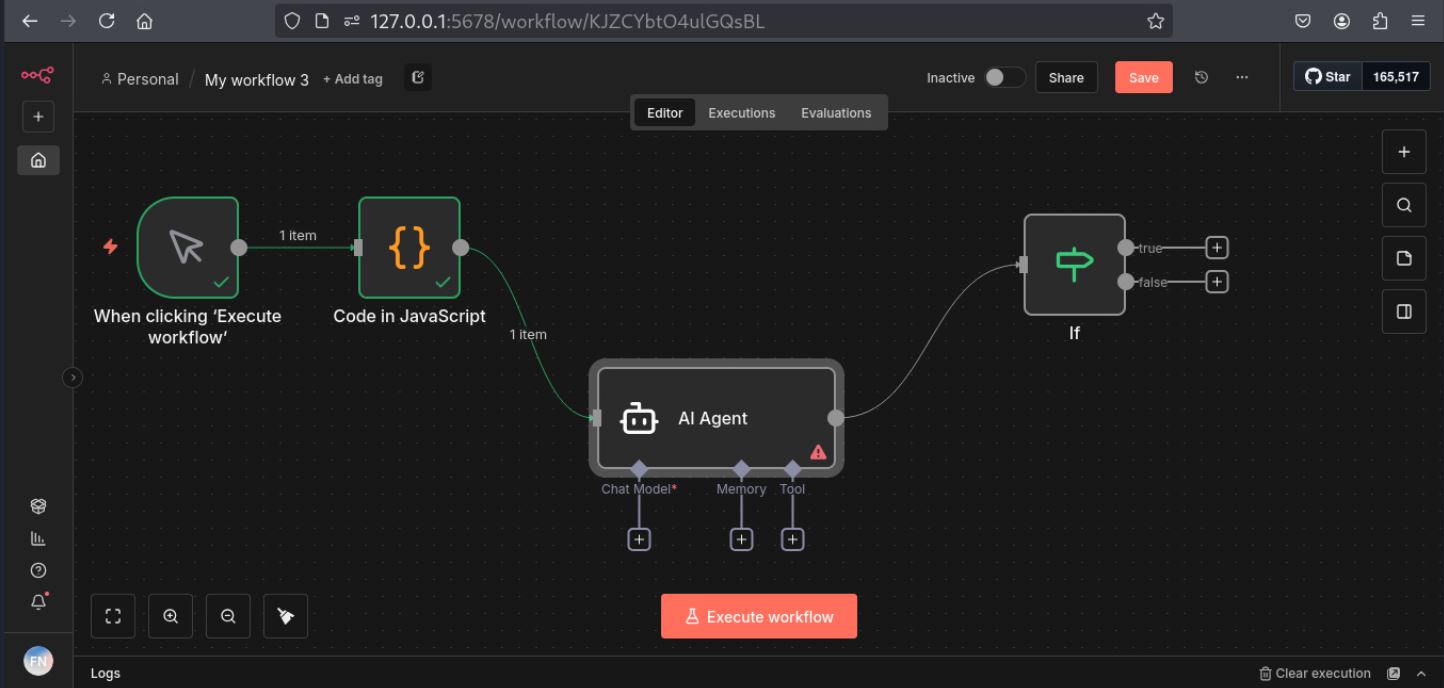
Triggering the Vulnerability
The core security flaw is an expression injection vulnerability that enables authenticated attackers to execute arbitrary JavaScript code with the privileges of the n8n process. Exploitation begins when an attacker gains authenticated access to an n8n instance with permission to create or edit workflows. This access level is commonly granted to developers, DevOps engineers, automation owners, and integration partners. In many environments, these permissions are shared broadly to support collaboration, increasing exposure in the event of credential compromise or insider misuse.
N8n Expression RCE Attack Flow involves below sequence:
- Access: An authenticated user who has the privilege to create or edit a workflow. Such access is provided to the lowest-privileged user working with an n8n AI instance. This step is of utmost concern as authentication does not play a major role in security, and workflow creation is considered a legitimate feature.
- Inject: The Expression Evaluation Engine accepts expressions inside {{}}. Adversaries will inject malicious payloads that contain executable logic. As this is the core part of the vulnerability, the payload gets executed without any validation from sandbox enforcement.
- Escape: The injected expressions escape the intended sandbox enforcement in an unsafe context allowing remote actors access to core Node.js modules and global runtime objects making this vulnerability more severe as the scope is changed.
- Execute: An attacker can execute remote commands as a legitimate user of the n8n instance.
In practice, an attacker with low-privilege permissions limited to workflow creation or editing could:
- Execute arbitrary operating-system commands.
- Steal sensitive secrets (API keys, tokens, passwords).
- Read or modify files on the host.
- Take full control of the underlying server.
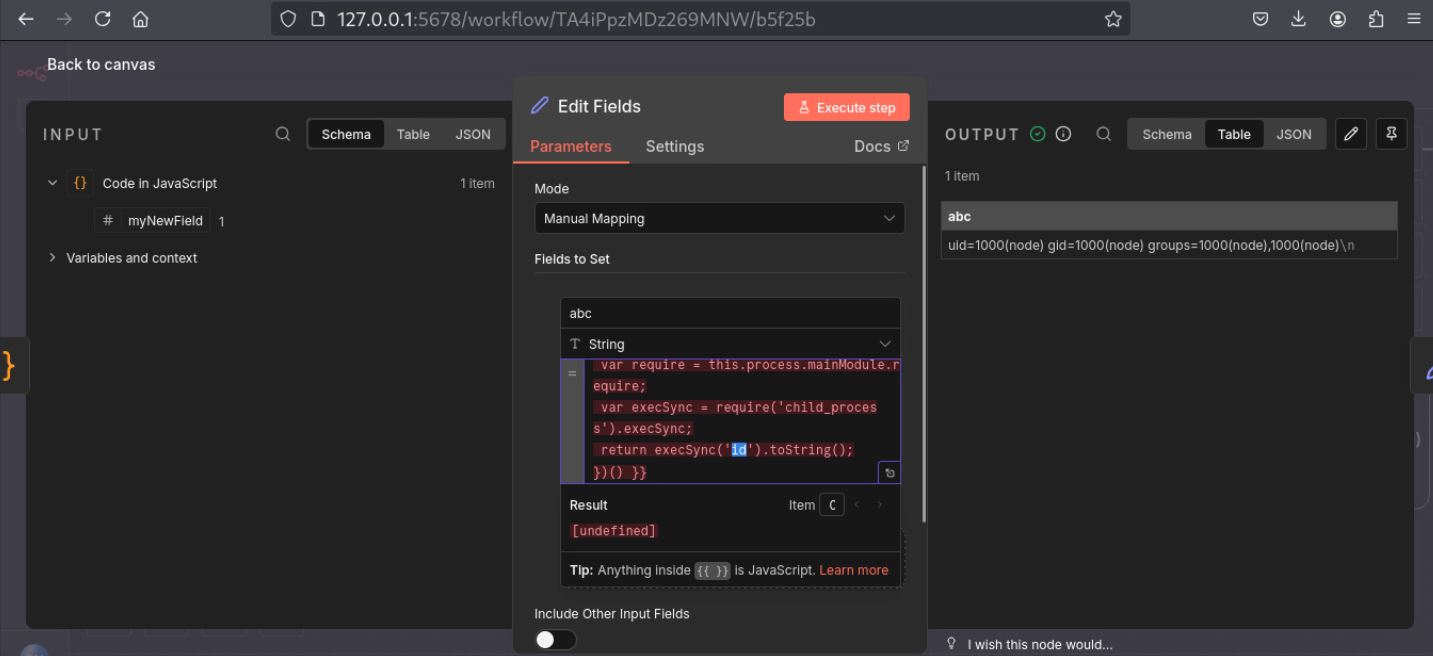
Exploitation
Successful exploitation of CVE-2025-12480 allows remote, authenticated attackers to achieve Remote Code Execution (RCE) in vulnerable N8n AI workflow instances. As demonstrated in Figure 3, an attacker with access to a vulnerable N8n platform initiates the exploit chain by creating or editing a node to start the workflow. Here, the “Set” node is used as a use-case scenario. Furthermore, the Field value is given a malicious expression input, a name, and then the command is executed. The result shows clear RCE. This ease of access with low-level privileges allows remote actors to create new nodes or upload malicious content to existing ones. The patched system will reject such requests, which introduces additional safeguards to restrict expression evaluation.
SonicWall Protections
To ensure SonicWall customers are prepared for any exploitation that may occur due to this vulnerability, the following signatures have been released:- IPS:21799 n8n Remote Code Execution
Remediation Recommendations
Given that adversary can circumvent access controls allowing them to create a new workflow with ease, users are strongly advised to upgrade their instances to the latest patched version as outlined in the official vendor advisory. If an immediate upgrade is not possible, consider implementing the following temporary workarounds:
- Limit workflow creation and editing permissions to fully trusted users only.
- Deploy n8n in a hardened environment with restricted operating system privileges and network access to reduce the impact of potential exploitation.
Relevant Links
Share This Article

An Article By
An Article By
Dhiren Vaghela
Dhiren Vaghela
Dhiren Vaghela has over a decade of experience in the IPS domain, with a strong focus on defensive security. His expertise lies in identifying, analyzing and mitigating vulnerabilities. Dhiren is well-versed in content-based signature writing, scanner-based alert generation and technical blog writing. By leveraging emerging technologies, he has developed numerous IPS signatures across various protocols. Known for his exceptional signature writing skills and collaborative team spirit, Dhiren is a valuable asset in the field of cybersecurity.
