Pre-Auth RCE Alert: Critical SSH Flaw in Erlang/OTP (CVE-2025-32433)

Overview
The SonicWall Capture Labs threat research team became aware of a pre-authentication vulnerability in Erlang/OTP (Open Telegram Platform) SSH server implementation, assessed its impact, and developed mitigation measures. Erlang/OTP is a known toolkit used to build scalable, fault-tolerant systems such as telecommunications, messaging platforms, IoT infrastructure and financial services. It is used by organizations like Ericsson, Cisco and WhatsApp.
Identified as CVE-2025-32433, Erlang/OTP SSH vulnerable versions include OTP 27.3.2 and earlier, OTP 26.2.5.10 and earlier, OTP 25.3.2.19 and earlier, and versions from OTP 17.0 and older. These vulnerable versions allow an attacker to be authenticated, verified and logged in as users because the server fails to properly reject certain types of protocol messages that are sent before the authentication phase of the SSH handshake. The SSH protocol message handling logic processes the request and executes the command as if it came from a trusted user. This makes the vulnerability critical, with a CVSS of 10 and EPSS of 67%. Given the availability of a public proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit and Erlang/OTP’s widespread use, the risk of exploitation is significantly elevated. Users are strongly urged to update to the latest patched versions immediately, as outlined in the vendor’s advisory, to protect against potential attacks.
Technical Overview
The vulnerability originates from the SSH server's failure to properly enforce authentication during the pre-authentication phase. Erlang/OTP’s built-in SSH server connection protocol messages, specifically SSH_MSG_CHANNEL_OPEN and SSH_MSG_CHANNEL_REQUEST, are the primary causes of this vulnerability. According to RFC 4254, these messages should be considered acceptable only after successful and legitimate authentication; any attempt to send them prematurely should result in the immediate termination of the connection. In the case of CVE-2025-34233, the SSH daemon fails to enforce this rule, allowing attackers to open a session channel and send an exec request containing arbitrary commands, all without supplying valid credentials or logging in. This means unauthenticated remote code execution (RCE), a fancy way of saying someone could hijack your server without knowing a single username, password or key.
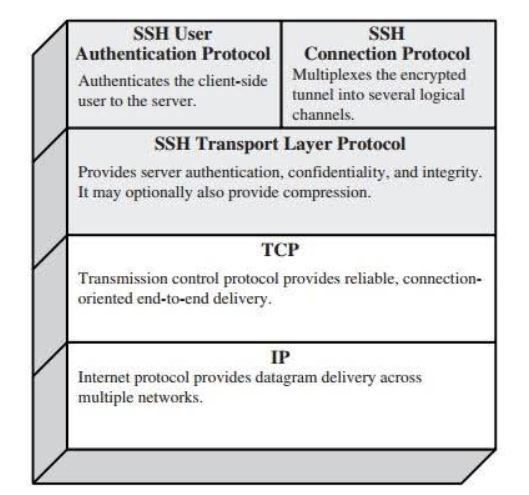
The SSH Connection Protocol operates on top of the SSH transport and user authentication layers. It provides features such as interactive logins, remote command execution and port forwarding. In the vulnerable Erlang/OTP SSH connection, the two relevant messages to initiate a channel connection and authenticate a user, are SSH_MSG_CHANNEL_OPEN and SSH_MSG_CHANNEL_REQUEST, which send requests over an established connection, are flawed. Due to this, an attacker can send crafted traffic that tricks the system into running malicious code without a login.
Exploitation
For the exploitation to work, one must find a vulnerable version of Erlang/OTP connected to the network and have SSH access.
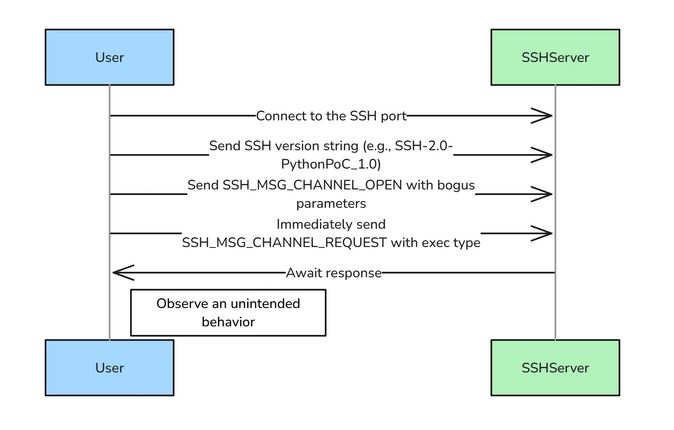
The exploit flow works as follows:
• In the Banner Exchange, the client and server exchange version strings and compatibility parameters as a standard process of the SSH connection protocol.
• The attacker conducts the key exchange negotiation by sending a crafted SSH_MSG_KEXINIT.
• By manipulating the authentication process, an attacker sends SSH_MSG_CHANNEL_OPEN to initiate a new session channel. Due to a failure to enforce authentication, this becomes the first part of the flaw, wherein an attacker tricks the SSH traffic to open a channel without any verification.
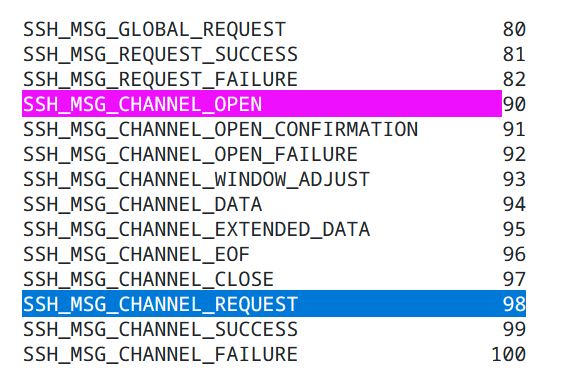
• The final step is sending SSH_MSG_CHANNEL_REQUEST (message number 98), which sends requests over an established channel, such as executing a command using the "exec" payload.
• The publicly available PoC demonstrates this by allowing remote, unauthenticated attackers to execute arbitrary shell commands to hijack user sessions, ultimately compromising accounts. This exploitation flow is illustrated in Figure 4.
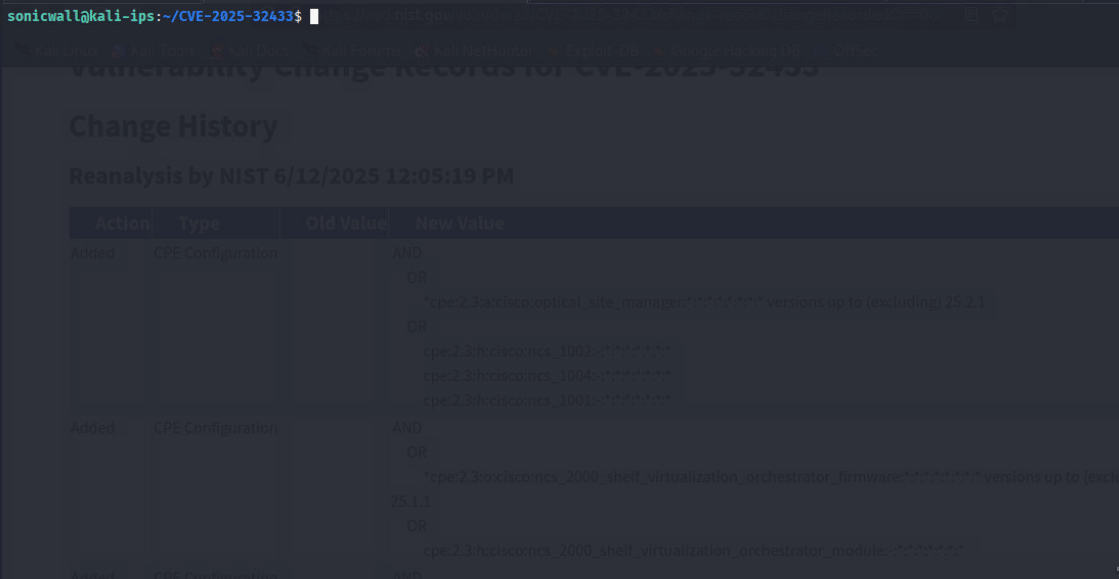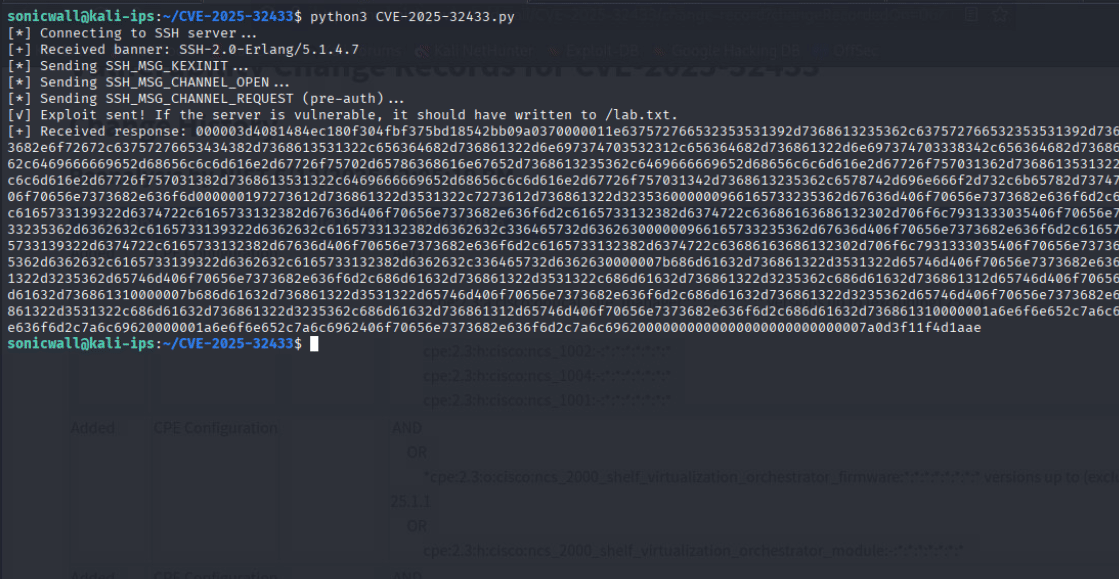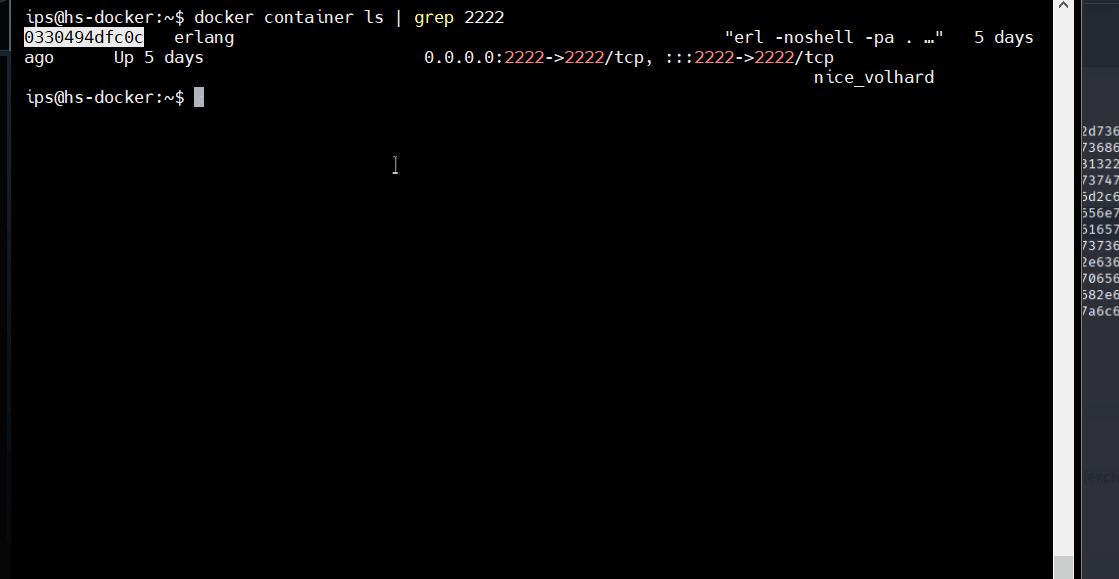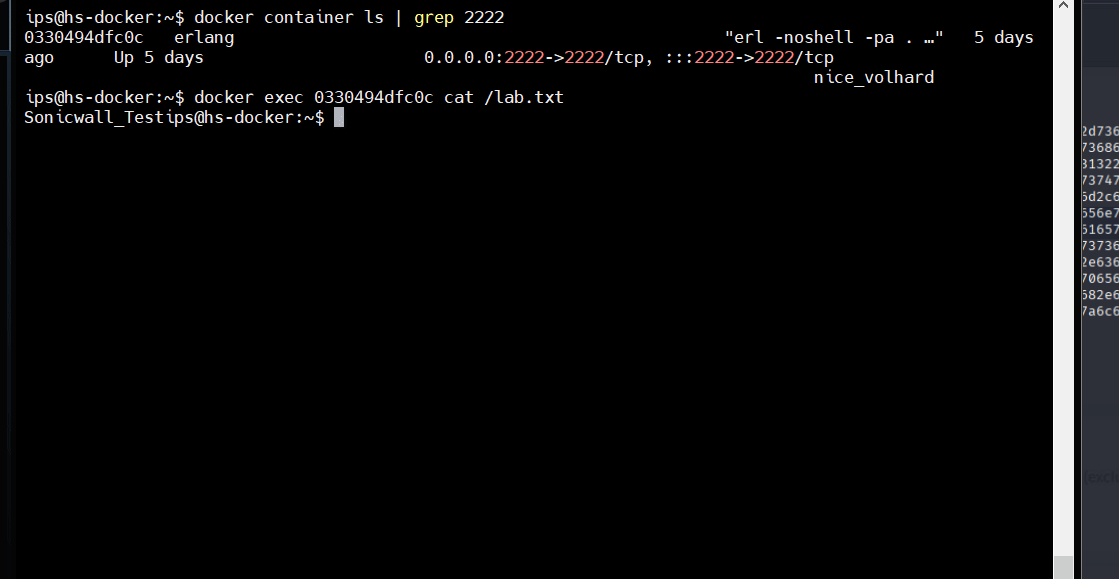
SonicWall Protections
To ensure SonicWall customers are prepared for any exploitation that may occur due to this vulnerability, the following signatures have been released:
IPS: 21127 Erlang OTP channel_request RCE
Remediation Recommendations
Erlang/OTP SSH users are strongly advised to upgrade their instances to the latest patched version as outlined in the official vendor advisory.
Relevant Links
Share This Article
An Article By
An Article By
Security News
Security News
